
Back بوكمينستر فوليرين Arabic فولرن باکمینستر AZB Бъкминстърфулерен Bulgarian ཐཱན༦༠ Tibetan Buckminsterfuleren BS Buckminsterful·lerè Catalan Buckminsterfulleren Czech Buckminsterfulleren Danish Μπακμίνστερφουλερένιο Greek Buckminsterfullereno Spanish
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌbʌkmɪnstərˈfʊləriːn/ | ||
| Preferred IUPAC name
(C60-Ih)[5,6]fullerene[1] | |||
| Other names
Buckyballs; Fullerene-C60; [60]fullerene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 5901022 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.884 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C60 | |||
| Molar mass | 720.660 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Dark needle-like crystals | ||
| Density | 1.65 g/cm3 | ||
| insoluble in water | |||
| Vapor pressure | 0.4–0.5 Pa (T ≈ 800 K); 14 Pa (T ≈ 900 K) [2] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Face-centered cubic, cF1924 | |||
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |||
a = 1.4154 nm
| |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
| Part of a series of articles on |
| Nanomaterials |
|---|
 |
| Carbon nanotubes |
| Fullerenes |
| Other nanoparticles |
| Nanostructured materials |
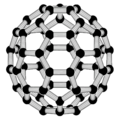
Buckminsterfullerene is a type of fullerene with the formula C60. It has a cage-like fused-ring structure (truncated icosahedron) made of twenty hexagons and twelve pentagons, and resembles a football. Each of its 60 carbon atoms is bonded to its three neighbors.
Buckminsterfullerene is a black solid that dissolves in hydrocarbon solvents to produce a violet solution. The substance was discovered in 1985 and has received intense study, although few real world applications have been found.
Molecules of buckminsterfullerene (or of fullerenes in general) are commonly nicknamed buckyballs.[3][4]
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 325. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Piacente; Gigli; Scardala; Giustini; Ferro (1995). "Vapor Pressure of C60 Buckminsterfullerene". J. Phys. Chem. 99 (38): 14052–14057. doi:10.1021/j100038a041.
- ^ "Buckyball". Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 13 April 2024.
- ^ The AZo Journal of Materials Online. AZoM.com. "Buckminsterfullerene." 2006.

