Back ثرومبين Arabic Trombin Azerbaijani Трамбін Byelorussian Трамбін BE-X-OLD Тромбин Bulgarian Trombin BS Trombina Catalan Thrombin Danish Thrombin German Trombina Spanish

Prothrombin (coagulation factor II) is encoded in the human by the F2-gene. It is proteolytically cleaved during the clotting process by the prothrombinase enzyme complex to form thrombin.
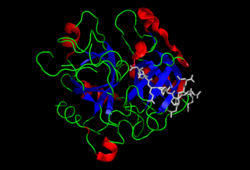
Thrombin (Factor IIa) (EC 3.4.21.5, fibrose, thrombase, thrombofort, topical, thrombin-C, tropostasin, activated blood-coagulation factor II, E thrombin, beta-thrombin, gamma-thrombin) is a serine protease, that converts fibrinogen into strands of insoluble fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions.[5][6]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000180210 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027249 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Royle NJ, Irwin DM, Koschinsky ML, MacGillivray RT, Hamerton JL (May 1987). "Human genes encoding prothrombin and ceruloplasmin map to 11p11-q12 and 3q21-24, respectively". Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics. 13 (3): 285–92. doi:10.1007/BF01535211. PMID 3474786. S2CID 45686258.
- ^ Degen SJ, Davie EW (September 1987). "Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human prothrombin". Biochemistry. 26 (19): 6165–77. doi:10.1021/bi00393a033. PMID 2825773.