| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
79 seats of the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia 40 seats were needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 55.44%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
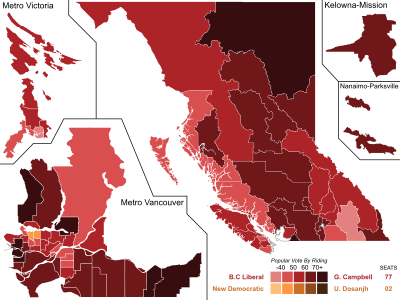 Popular vote by riding. As this is an FPTP election, seat totals are not determined by popular vote, but instead via results by each riding. Click the map for more details. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2001 British Columbia general election was the 37th provincial election in the Province of British Columbia, Canada. It was held to elect members of the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia. The election was called on April 18, 2001 and held on May 16, 2001. Voter turnout was 55.4 per cent of all eligible voters.
The incumbent British Columbia New Democratic Party (BC NDP), in office since 1991, had been rocked by two major scandals—the Fast Ferries Scandal and a bribery scandal involving Premier Glen Clark. With the NDP's ratings flatlining, Clark resigned in August 1999, and Deputy Premier Dan Miller took over as caretaker premier until Ujjal Dosanjh was elected his permanent successor in February. Dosanjh was not, however, able to restore the party's public image, and the BC NDP suffered a resounding defeat at the hands of the British Columbia Liberal Party (BC Liberals), led by former Vancouver mayor Gordon Campbell. The BC Liberals won over 57% of the popular vote, and an unprecedented 77 of the 79 seats in the provincial legislature—the largest victory in the province's electoral history.
The BC NDP, on the other hand, suffered a near-total political collapse. The party lost almost half of the share of the popular vote that it had won in the 1996 election, while its seat count fell from 39 seats to only two—those of Deputy Premier and Education Minister Joy MacPhail and Community Development Minister Jenny Kwan. It was easily the worst defeat of a sitting government in British Columbia history. It was also the second-worst defeat of a sitting provincial government in Canada, eclipsed only by the New Brunswick election of 1987, the Alberta election of 1935, and the Prince Edward Island election of 1935. In those elections, the governing party–the New Brunswick Tories, the United Farmers of Alberta and the PEI Tories–was completely wiped off the map. Dosanjh resigned as party leader soon after the election; he had actually conceded defeat a week before voters went to the polls. Despite being the only other party in the Assembly, the BC NDP lacked the four seats then required for official party status.[2]
The British Columbia Unity Party had been created as a union of conservative parties. Initially, Reform BC, the Social Credit, the British Columbia Party, and the Family Coalition Party had joined under the "BC Unity" umbrella. By the time the election was called, however, only the Family Coalition Party and a large majority of Reform BC segments had remained in the BC Unity coalition. The other parties had withdrawn to continue independently. The parties would collectively only earn around 4% of the vote, as voters, conscious of vote-splitting that had taken place between the Liberals, Reform BC, and the since-defunct Progressive Democratic Alliance in 1996, united behind the Liberals this time. Ron Gamble, sometime leader and sometime president of the renewed Reform BC continued his opposition to conservative mergers, consistently proclaiming a "Say No to Chris Delaney & BC Unity" policy, until Unity's eventual collapse in 2004 after a failed second attempt at a merger with BC Conservatives.
- ^ "B.C. Voter Participation: 1983 to 2013" (PDF). Elections BC. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 28, 2019. Retrieved May 11, 2017.
- ^ "B.C. NDP no longer official party after recounts". CBC News. May 31, 2001. Retrieved October 31, 2012.



