Back Eleccions generals del Brasil de 2022 Catalan Wahlen in Brasilien 2022 German Βραζιλιάνικες γενικές εκλογές 2022 Greek Elecciones generales de Brasil de 2022 Spanish 2022ko Brasilgo hauteskunde orokorrak Basque انتخابات سراسری برزیل (۲۰۲۲) Persian Brasilian yleisvaalit 2022 Finnish Élections parlementaires brésiliennes de 2022 French Olltoghchán na Brasaíle, 2022 Irish הבחירות הכלליות בברזיל (2022) HE
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 79.05% (first round) 79.41% (second round) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 513 seats in the Chamber of Deputies 257 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
27 of the 81 seats in the Federal Senate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General elections were held in Brazil on 2 October 2022 to elect the president, vice president, the National Congress, the governors, vice governors, and legislative assemblies of all federative units, and the district council of Fernando de Noronha. As no candidate for president—or for governor in some states—received more than half of the valid votes in the first round, a runoff election for these offices was held on 30 October. Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva received the majority of the votes in the second round and became president-elect of Brazil.
Incumbent president Jair Bolsonaro was seeking a second term. He had been elected in 2018 as the candidate of the Social Liberal Party but left that party in 2019, followed by the resignation or dismissal of many of his ministers during his term. After a failed attempt to create the Alliance for Brazil, he joined the Liberal Party in 2021. For the 2022 election, he selected Walter Braga Netto of the same party as his vice presidential candidate rather than the incumbent vice president Hamilton Mourão.
Former president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, of the left-wing Workers' Party, was a candidate for a third non-consecutive term after previously having been elected in 2002 and re-elected in 2006. His successor from the same party, former president Dilma Rousseff, was elected in 2010 and re-elected in 2014, but was impeached and removed from office in 2016 due to accusations of administrative misconduct. Lula's intended candidacy in 2018 was disallowed due to his conviction on corruption charges in 2017 and subsequent arrest; a series of court rulings led to his release from prison in 2019, followed by the annulment of his conviction and restoration of his political rights by 2021. For his vice presidential candidate in the 2022 election, Lula selected Geraldo Alckmin, who had been a presidential candidate of the Brazilian Social Democracy Party in 2006 (facing Lula in the second round) and 2018 but changed his affiliation to the Brazilian Socialist Party in 2022.[1]
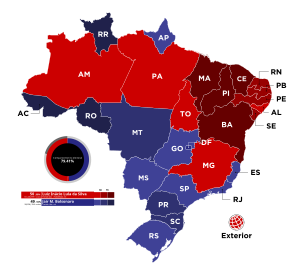
Lula received the most votes in the first round, with 48.43% to Bolsonaro's 43.20%, which made him the first presidential candidate to obtain more votes than the incumbent president in Brazil. While Lula came close to winning in the first round, the difference between the two leading candidates was closer than opinion polls had suggested, and right-wing parties made gains in the National Congress. Nevertheless, Lula's vote share was the second-best performance for the Workers' Party in the first round of a presidential election, behind only his own record of 48.61% in 2006. In the second round, Lula received 50.90% of the votes to Bolsonaro's 49.10%, the closest presidential election result in Brazil to date. Lula became the first person to secure a third presidential term, receiving the highest number of votes in a Brazilian election. At the same time, Bolsonaro became the first incumbent president to lose a bid for a second term since a 1997 constitutional amendment allowing consecutive re-election.
In response to Lula's advantage in pre-election polls, Bolsonaro had made several pre-emptive allegations of electoral fraud. Many observers denounced these allegations as false and expressed concerns that they could be used to challenge the outcome of the election. On 1 November, during his first public remarks after the election, Bolsonaro refused to elaborate on the result, although he did authorise his chief of staff, Ciro Nogueira Lima Filho, to begin the transition process with representatives of president-elect Lula on 3 November. On 22 November, Bolsonaro and his party requested that the Superior Electoral Court invalidate the votes recorded by electronic voting machines that lacked identification numbers, which would have resulted in him being elected with 51% of the remaining votes. On the next day the court rejected the request and fined the party R$22.9 million (US$4.3 million) for what it considered bad faith litigation. Lula was sworn in on 1 January 2023; a week later, pro-Bolsonaro protestors stormed the offices of the National Congress, the Presidential Palace, and the Supreme Federal Court, unsuccessfully attempting to overthrow the newly elected government. The elected members of the National Congress were sworn in on 1 February.[2]
The documentary 'Apocalypse in the Tropics' (2024) shows how evangelical pastor Silas Malafaia had a defining influence on Bolsanaro, while mustering support from Brasil's evangelical movement, in the path to the election and in the protests and attempted insurrection that followed.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Boadle, Anthony (23 March 2022). "Former Sao Paulo governor Alckmin joins leftist party to be Lula's running mate". Reuters. Archived from the original on 4 November 2022. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
- ^ "Veja como ficam as bancadas na Câmara dos Deputados e no Senado" [See how the benches in the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate look]. Jovem Pan (in Brazilian Portuguese). 1 February 2023. Retrieved 3 February 2023.