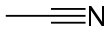Back أسيتونتريل Arabic استونیتریل AZB Acetonitril Catalan Acetonitril Czech Acetonitril Danish Acetonitril German Αιθανονιτρίλιο Greek Acetonitrilo Esperanto Acetonitrilo Spanish Atsetonitriil Estonian
| |||
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Acetonitrile[2] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethanenitrile[2] | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 741857 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.760 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 895 | |||
| MeSH | acetonitrile | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1648 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H3N | |||
| Molar mass | 41.053 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Faint, distinct, fruity | ||
| Density | 0.786 g/cm3 at 25°C | ||
| Melting point | −46 to −44 °C; −51 to −47 °F; 227 to 229 K | ||
| Boiling point | 81.3 to 82.1 °C; 178.2 to 179.7 °F; 354.4 to 355.2 K | ||
| Miscible | |||
| log P | −0.334 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 9.71 kPa (at 20.0 °C) | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
530 μmol/(Pa·kg) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 25 | ||
| UV-vis (λmax) | 195 nm | ||
| Absorbance | ≤0.10 | ||
| −28.0×10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.344 | ||
| 3.92 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
91.69 J/(K·mol) | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
149.62 J/(K·mol) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
40.16–40.96 kJ/mol | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−1256.03 – −1256.63 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H302, H312, H319, H332 | |||
| P210, P280, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 2.0 °C (35.6 °F; 275.1 K) | ||
| 523.0 °C (973.4 °F; 796.1 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 4.4–16.0% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
| ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
5655 ppm (guinea pig, 4 hr) 2828 ppm (rabbit, 4 hr) 53,000 ppm (rat, 30 min) 7500 ppm (rat, 8 hr) 2693 ppm (mouse, 1 hr)[4] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
16,000 ppm (dog, 4 hr)[4] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 40 ppm (70 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 20 ppm (34 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
500 ppm[3] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanenitriles
|
|||
Related compounds
|
DBNPA | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Acetonitrile (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
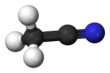
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula CH3CN and structure H3C−C≡N. This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene.[5] The N≡C−C skeleton is linear with a short C≡N distance of 1.16 Å.[6]
Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas.[7]
- ^ a b c d "Material Safety Data Sheet: Acetonitrile" (PDF). TedPella.com.
- ^ a b Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 902. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0006". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b "Acetonitrile". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, Third edition. p. 76. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-16. Retrieved 2011-03-31.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Karakida, Ken'ichi; Fukuyama, Tsutomu; Kuchitsu, Kozo (1974). "Molecular Structures of Hydrogen Cyanide and Acetonitrile as Studied by Gas Electron Diffraction". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 47 (2): 299–304. doi:10.1246/bcsj.47.299.
- ^ Dumas, J.-B. (1847). "Action de l'acide phosphorique anhydre sur les sels ammoniacaux" [Action of anhydrous phosphoric acid on ammonium salts]. Comptes rendus. 25: 383–384.