Back أكريلونتريل Arabic Akrilnitril Azerbaijani اکریلونیتریل AZB Acrilonitril Catalan Akrylonitril Czech Acrylnitril German Ακρυλονιτρίλιο Greek Akrilonitrilo Esperanto Acrilonitrilo Spanish Akrilonitrilo Basque
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Prop-2-enenitrile | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.152 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1093 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H3N | |||
| Molar mass | 53.064 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.81 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −84 °C (−119 °F; 189 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 77 °C (171 °F; 350 K) | ||
| 70 g/L | |||
| log P | 0.19[2] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 83 mmHg[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
flammable reactive toxic potential occupational carcinogen[1] | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −1 °C; 30 °F; 272 K | ||
| 471 °C (880 °F; 744 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 3–17% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
500 ppm (rat, 4 h) 313 ppm (mouse, 4 h) 425 ppm (rat, 4 h)[3] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
260 ppm (rabbit, 4 h) 575 ppm (guinea pig, 4 h) 636 ppm (rat, 4 h) 452 ppm (human, 1 h)[3] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 2 ppm C 10 ppm [15-minute] [skin][1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca TWA 1 ppm C 10 ppm [15-minute] [skin][1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
85 ppm[1] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0092 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related nitriles
|
acetonitrile propionitrile | ||
Related compounds
|
acrylic acid acrolein | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
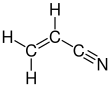
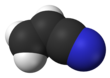
Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHCN and the structure H2C=CH−C≡N. It is a colorless, volatile liquid. It has a pungent odor of garlic or onions.[4] Its molecular structure consists of a vinyl group (−CH=CH2) linked to a nitrile (−C≡N). It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics such as polyacrylonitrile. It is reactive and toxic at low doses.[5]
Acrylonitrile is one of the components of ABS plastic (Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene).[6]
- ^ a b c d e f g h NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0014". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Acrylonitrile_msds".
- ^ a b "Acrylonitrile". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Medical Management Guidelines for Acrylonitrile". Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. Retrieved 2020-06-10.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Campo, E. Alfredo (2008-01-01), Campo, E. Alfredo (ed.), "1 - Polymeric Materials and Properties", Selection of Polymeric Materials, Plastics Design Library, Norwich, NY: William Andrew Publishing, pp. 1–39, doi:10.1016/b978-081551551-7.50003-6, ISBN 978-0-8155-1551-7, retrieved 2023-11-20