
Back ألمانيا المحتلة من قبل قوات الحلفاء Arabic المانيا المحتله من قوات التحالف ARZ Ocupación aliada d'Alemaña AST 1945–1949-cu illərdə Almaniya Azerbaijani ایشغال آلمانی AZB Окупирана от Съюзниците Германия Bulgarian Zones d'ocupació aliada a Alemanya Catalan Okupační zóny Německa Czech Besættelseszoner i Tyskland efter 2. verdenskrig Danish Deutschland 1945 bis 1949 German
Germany Deutschland (German) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1945–1949 | |||||||||||||
|
The C-Pennant | |||||||||||||
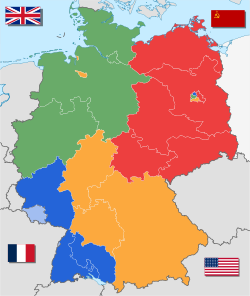 Germany from 17 December 1947 to 23 May 1949 | |||||||||||||
| Status | Military occupation | ||||||||||||
| Capital |
52°31′N 13°23′E / 52.517°N 13.383°E Saar Protectorate (de facto not a part of Germany) French occupation zone British occupation zone[a] American occupation zone Soviet occupation zone[b] | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | |||||||||||||
| Governors (1945) | |||||||||||||
• British zone | Bernard Montgomery | ||||||||||||
• American zone | Dwight D. Eisenhower | ||||||||||||
• French zone | Jean de Lattre de Tassigny | ||||||||||||
• Soviet zone | Georgy Zhukov | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||||
| 8 May 1945 | |||||||||||||
| 5 June 1945 | |||||||||||||
| 17 December 1947 | |||||||||||||
| 23 May 1949 | |||||||||||||
• East Germanyb | 7 October 1949 | ||||||||||||
| 15 March 1991 | |||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||
• 1945 | 64,260,000 | ||||||||||||
• 1949 | 68,080,000 | ||||||||||||
| Currency |
| ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| History of Germany |
|---|
 |
The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II, from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Nazi Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Germany formally surrendered on 8 May 1945, the four countries representing the Allies (the United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and France) asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC).
At first, Allied-occupied Germany was defined as all territories of Germany before the 1938 Nazi annexation of Austria. The Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945 defined the new eastern German border by giving Poland and the Soviet Union all regions of Germany east of the Oder–Neisse line (eastern parts of Pomerania, Neumark, Posen-West Prussia, East-Prussia and most of Silesia) and divided the remaining "Germany as a whole" into four occupation zones, each administered by one of the Allies.[1]
All territories annexed by Germany before the war from Austria and Czechoslovakia were returned to these countries. The Memel Territory, annexed by Germany from Lithuania before the war, was annexed by the Soviet Union in 1945 and transferred to the Lithuanian SSR. All territories annexed by Germany during the war from Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, Poland and Yugoslavia were returned to their respective countries.
Deviating from the occupation zones planned according to the London Protocol in 1944, at Potsdam, the United States, United Kingdom and the Soviet Union approved the detachment from Germany of the territories east of the Oder–Neisse line, with the exact line of the boundary to be determined in a final German peace treaty. This treaty was expected to confirm the shifting westward of Poland's borders, as the United Kingdom and United States committed themselves to support the permanent incorporation of eastern Germany into Poland and the Soviet Union. From March 1945 to July 1945, these former eastern territories of Germany had been administered under Soviet military occupation authorities, but following the Potsdam Agreement they were handed over to Soviet and Polish civilian administrations and ceased to constitute part of Allied-occupied Germany.
In the closing weeks of fighting in Europe, United States forces had pushed beyond the agreed boundaries for the future zones of occupation, in some places by as much as 320 km (200 miles). The so-called line of contact between Soviet and U.S. forces at the end of hostilities, mostly lying eastward of the July 1945-established inner German border, was temporary.
After two months during which they held areas that had been assigned to the Soviet zone, U.S. forces withdrew in the first days of July 1945.[2] Some have concluded that this was a crucial move which persuaded the Soviet Union to allow American, British and French forces into their designated sectors in Berlin, which occurred at roughly the same time; the need for intelligence gathering (Operation Paperclip) may also have been a factor.[3]
On 20 March 1948, the Soviets withdrew from the Allied Control Council. The split led to the establishment in 1949 of two new German states, West Germany and East Germany.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ States, United (1968). Treaties and Other International Agreements of the United States of America, 1776-1949: Multilateral, 1931-1945. Department of State. Archived from the original on 21 January 2023. Retrieved 24 June 2021.
- ^ "What Is to Be Done?". Time. 9 July 1945. Archived from the original on 16 February 2023. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Knowles, Chris (29 January 2014). "Germany 1945–1949: a case study in post-conflict reconstruction". History & Policy. Archived from the original on 9 June 2023. Retrieved 19 July 2016.

