
Back Alpensteinbock ALS وعل ألبي Arabic وعل البى ARZ Alpaf deaxelol (Capra ibex) AVK Alp dağ keçisi Azerbaijani Stoaboog BAR Алпийски козирог Bulgarian ཁབ་ར། Tibetan Kragvouc'h an Alpoù Breton Cabra dels Alps Catalan
| Alpine ibex | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male | |

| |
| Female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Caprinae |
| Tribe: | Caprini |
| Genus: | Capra |
| Species: | C. ibex
|
| Binomial name | |
| Capra ibex | |
| |
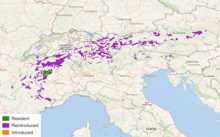
| Distribution of the Alpine ibex (population in Bulgaria not included) | |
The Alpine ibex (Capra ibex), also known as the steinbock, is a European species of goat that lives in the Alps. It is one of ten species in the genus Capra and its closest living relative is the Iberian ibex. The Alpine ibex is a sexually dimorphic species; males are larger and carry longer horns than females. Its coat is brownish-grey. Alpine ibexes tend to live in steep, rough terrain and open alpine meadows. They can be found at elevations as high as 3,300 m (10,800 ft) and their sharp hooves allow them to scale the steep slopes and cliffs of their mountainous habitat.
Alpine ibexes primarily feed on grass and are active throughout the year. Although they are social animals, adult males and females segregate for most of the year, coming together only to mate. During the breeding season, males use their long horns to fight for access to females. Ibexes have few predators but may succumb to parasites and diseases.
By the 19th century, the Alpine ibex had been extirpated from most of its range and it went through a population bottleneck of fewer than 100 individuals during its near-extinction event, leading to very low genetic diversity across populations. The species has been successfully reintroduced to parts of its historical range. All individuals living today descend from the stock in Gran Paradiso National Park, Italy. As of 2020[update], the IUCN lists the species as being of least concern.
- ^ Toïgo, C.; Brambilla, A.; Grignolio, S.; Pedrotti, L. (2020). "Capra ibex". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T42397A161916377. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T42397A161916377.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
