
Back قشرة حزامية أمامية Arabic Córtex del cíngulo anterior Spanish Cortex cingulaire antérieur French פיתול החגורה הקדמי HE Corteccia cingolata anteriore Italian 前帯状皮質 Japanese Priekšējā cingulārā garoza Latvian/Lettish Cortex cingularis anterior Dutch Córtex cingulado anterior Portuguese Передняя поясная кора Russian
| Anterior cingulate cortex | |
|---|---|
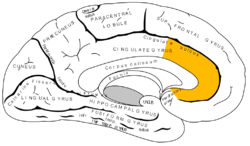 Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted | |
 Medial surface of right hemisphere, with Brodmann's areas numbered | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cortex cingularis anterior |
| NeuroNames | 161 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_936 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
In the human brain, the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex that resembles a "collar" surrounding the frontal part of the corpus callosum. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32, and 33.
It is involved in certain higher-level functions, such as attention allocation,[1] reward anticipation, decision-making, impulse control (e.g. performance monitoring and error detection),[2] and emotion.[3][4]
Some research calls it the anterior midcingulate cortex (aMCC).

- ^ Pardo JV, Pardo PJ, Janer KW, Raichle ME (January 1990). "The anterior cingulate cortex mediates processing selection in the Stroop attentional conflict paradigm". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 87 (1): 256–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87..256P. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.1.256. PMC 53241. PMID 2296583.
- ^ Hewitt J (26 March 2013). "Predicting repeat offenders with brain scans: You be the judge". medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ Decety J, Jackson PL (June 2004). "The functional architecture of human empathy". Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews. 3 (2): 71–100. doi:10.1177/1534582304267187. PMID 15537986. S2CID 145310279.
- ^ Jackson PL, Brunet E, Meltzoff AN, Decety J (2006). "Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain" (PDF). Neuropsychologia. 44 (5): 752–61. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.333.2783. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.07.015. PMID 16140345. S2CID 6848345. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2019.