
Back داء الأسكارس Arabic الاسكارس ARZ Askaridoz Azerbaijani Аскарыдоз Byelorussian Аскариоза Bulgarian অ্যাসক্যারিয়াসিস Bengali/Bangla Askarijaza BS Ascariosi Catalan Askarióza Czech Askariasis Danish
| Ascariasis | |
|---|---|
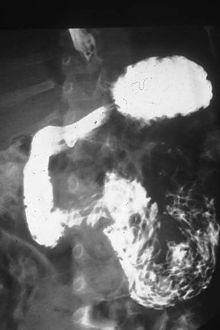 | |
| High number of ascaris worms – visible as black tangled mass – are filling the duodenum, the first portion of the bowel after the stomach, of this South African patient (X-ray image with barium as contrast medium). | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, diarrhea, shortness of breath[1] |
| Causes | Ingestion of Ascaris eggs[2] |
| Prevention | Improved sanitation, handwashing[1] |
| Medication | Albendazole, mebendazole, levamisole, pyrantel pamoate[2] |
| Frequency | 762 million (2015)[3] |
| Deaths | 2,700 (2015)[4] |
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides.[1] Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small.[1] Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may include shortness of breath and fever in the beginning of the disease.[1] These may be followed by symptoms of abdominal swelling, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.[1] Children are most commonly affected, and in this age group the infection may also cause poor weight gain, malnutrition, and learning problems.[1][2][5]
Infection occurs by ingestion of food or drink contaminated with Ascaris eggs from feces.[2] The eggs hatch in the intestines, the larvae burrow through the gut wall, and migrate to the lungs via the blood.[2] There they break into the alveoli and pass up the trachea, where they are coughed up and may be swallowed.[2] The larvae then pass through the stomach for a second time into the intestine, where they become adult worms.[2] It is a type of soil-transmitted helminthiasis and part of a group of diseases called helminthiases.[6]
Prevention is by improved sanitation, which includes improving access to toilets and proper disposal of feces.[1][7] Handwashing with soap appears protective.[8] In areas where more than 20% of the population is affected, treating everyone at regular intervals is recommended.[1] Reoccurring infections are common.[2][9] There is no vaccine.[2] Treatments recommended by the World Health Organization are the medications albendazole, mebendazole, levamisole, or pyrantel pamoate.[2] Other effective agents include tribendimidine and nitazoxanide.[2]
About 0.8 to 1.2 billion people globally have ascariasis, with the most heavily affected populations being in sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, and Asia.[1][10][11] This makes ascariasis the most common form of soil-transmitted helminthiasis.[10] As of 2010 it caused about 2,700 deaths a year, down from 3,400 in 1990.[12] Another type of Ascaris infects pigs.[1] Ascariasis is classified as a neglected tropical disease.[6]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Dold C, Holland CV (July 2011). "Ascaris and ascariasis". Microbes and Infection. 13 (7): 632–7. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2010.09.012. hdl:2262/53278. PMID 20934531.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Hagel I, Giusti T (October 2010). "Ascaris lumbricoides: an overview of therapeutic targets". Infectious Disorders Drug Targets. 10 (5): 349–67. doi:10.2174/187152610793180876. PMID 20701574.
- ^ Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. (GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ^ Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, et al. (GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- ^ "Soil-transmitted helminth infections Fact sheet N°366". World Health Organization. June 2013. Archived from the original on 2014-02-21.
- ^ a b "Neglected Tropical Diseases". cdc.gov. June 6, 2011. Archived from the original on 4 December 2014. Retrieved 28 November 2014.
- ^ Ziegelbauer K, Speich B, Mäusezahl D, Bos R, Keiser J, Utzinger J (January 2012). "Effect of sanitation on soil-transmitted helminth infection: systematic review and meta-analysis". PLOS Medicine. 9 (1): e1001162. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001162. PMC 3265535. PMID 22291577.
- ^ Fung IC, Cairncross S (March 2009). "Ascariasis and handwashing". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 103 (3): 215–22. doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2008.08.003. PMID 18789465.
- ^ Jia TW, Melville S, Utzinger J, King CH, Zhou XN (2012). "Soil-transmitted helminth reinfection after drug treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 6 (5): e1621. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001621. PMC 3348161. PMID 22590656.
- ^ a b Keiser J, Utzinger J (2010). "The drugs we have and the drugs we need against major helminth infections". Advances in Parasitology. 73: 197–230. doi:10.1016/s0065-308x(10)73008-6. ISBN 978-0-12-381514-9. PMID 20627144.
- ^ Fenwick A (March 2012). "The global burden of neglected tropical diseases". Public Health. 126 (3): 233–236. doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2011.11.015. PMID 22325616.
- ^ Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. (December 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30050819. PMC 10790329. PMID 23245604. S2CID 1541253.