
Back Astronomiese eenheid Afrikaans Astronomische Einheit ALS Unidat astronomica AN وحدة فلكية Arabic عبرة فلكية ARY وحده فلكيه ARZ Unidá astronómica AST Astronomik vahid Azerbaijani آسترونومیک واحید AZB Астранамічная адзінка Byelorussian
| Astronomical unit | |
|---|---|
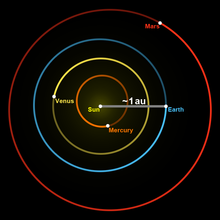 The grey line indicates the Earth–Sun distance, which on average is about 1 astronomical unit. | |
| General information | |
| Unit system | Astronomical system of units (Accepted for use with the SI) |
| Unit of | length |
| Symbol | au or AU or AU |
| Conversions | |
| 1 au or AU or AU in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| metric (SI) units | 1.495978707×1011 m |
| imperial & US units | 9.2956×107 mi |
| astronomical units | 4.8481×10−6 pc 1.5813×10−5 ly 215.03 R☉ |
The astronomical unit (symbol: au[1][2][3][4] or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to 149,597,870,700 m.[5] Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its modern redefinition in 2012.
The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec.[6] One au is equivalent to 499 light-seconds to within 10 parts per million.
- ^ On the re-definition of the astronomical unit of length (PDF). XXVIII General Assembly of International Astronomical Union. Beijing, China: International Astronomical Union. 31 August 2012. Resolution B2.
... recommends ... 5. that the unique symbol "au" be used for the astronomical unit.
- ^ "Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Instructions for Authors". Oxford Journals. Archived from the original on 22 October 2012. Retrieved 20 March 2015.
The units of length/distance are Å, nm, μm, mm, cm, m, km, au, light-year, pc.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
AAS_stylewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The International System of Units (PDF) (9th ed.), International Bureau of Weights and Measures, December 2022, p. 145, ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0
- ^ On the re-definition of the astronomical unit of length (PDF). XXVIII General Assembly of International Astronomical Union. Beijing: International Astronomical Union. 31 August 2012. Resolution B2.
... recommends [adopted] that the astronomical unit be re-defined to be a conventional unit of length equal to exactly 149,597,870,700 metres, in agreement with the value adopted in IAU 2009 Resolution B2
- ^ Luque, B.; Ballesteros, F.J. (2019). "Title: To the Sun and beyond". Nature Physics. 15: 1302. doi:10.1038/s41567-019-0685-3.