
Back مكاك مقلنس Arabic مكاك مقلنس ARZ Lilkol (Macaca radiata) AVK Macaca radiata Bulgarian Macaca radiata Breton Macaco de capell Catalan Macaca radiata CEB Makak kápový Czech Indischer Hutaffe German Macaca radiata Spanish
| Bonnet macaque | |
|---|---|

| |
| Bonnet macaque (Macaca radiata), Mangaon, Maharashtra, India | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Cercopithecidae |
| Genus: | Macaca |
| Species: | M. radiata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Macaca radiata (É. Geoffroy, 1812)
| |
| |
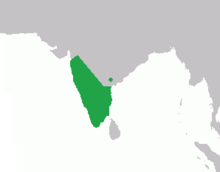
| Bonnet macaque range | |
| Synonyms | |
| |

The bonnet macaque (Macaca radiata), also known as zati,[2] is a species of macaque endemic to southern India. Its distribution is limited by the Indian Ocean on three sides and the Godavari and Tapti Rivers, along with its related competitor the rhesus macaque in the north.[1][3][4] Land use changes in the last few decades have resulted in changes in its distribution boundaries with the rhesus macaque, raising concern for its status in the wild.[5][6]
The bonnet macaque is diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrial. Males have a head-body length of 51.5–60 cm (20.3–23.6 in) with a 51–69 cm (20–27 in) tail while females are 34.5–52.5 cm (13.6–20.7 in) with a 48–63.5 cm (18.9–25.0 in) tail. Males weigh 5.4–11.6 kg (12–26 lb) and females 2.9–5.5 kg (6.4–12.1 lb).[7] It can live up to 35 years in captivity.[8]
The bonnet macaque feeds on fruits, nuts, seeds, flowers, invertebrates, and cereals. In southern India, this macaque exists as commensal to humans, feeding on food given by humans and raiding crops and houses.[8]
- ^ a b Singh, M.; Kumara, H.N.; Kumar, A. (2020). "Macaca radiata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T12558A17951596. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T12558A17951596.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ Chambers English Dictionary
- ^ Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 164. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Fooden, Jack (1988). "Taxonomy and evolution of the sinica group of macaques : 6. Interspecific comparisons and synthesis". Fieldiana Zoology. New Series. 45: 1–44. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.2841.
- ^ Kumar, R. Radhakrishna; S. Sinha, A. (2011). "Of Least Concern? Range extension by rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) threatens long-term survival of bonnet macaques (M. radiata) in Peninsular India". International Journal of Primatology. 32 (4): 945. doi:10.1007/s10764-011-9514-y. S2CID 35227050.
- ^ Govindarajan, Vinita. "South India is losing its endemic bonnet monkey to an aggressive invader from the north". Scroll.in. Retrieved 2017-09-14.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Anandam2013was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Brown, M. (2008). "Macaca radiata". Animal Diversity Web.
