
Back لمفوما بيركت Arabic Burkittov limfom BS Limfoma de Burkitt Catalan Burkittův lymfom Czech Burkitt-Lymphom German Λέμφωμα του Μπέρκετ Greek Linfoma de Burkitt Spanish Burkitten linfoma Basque لنفوم بورکیت Persian Burkittin lymfooma Finnish
| Burkitt lymphoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Burkitt's tumor, Burkitt's lymphoma, malignant lymphoma Burkitt's type |
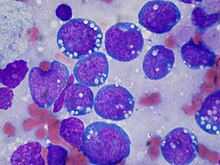 | |
| Burkitt lymphoma, touch prep, Wright stain | |
| Specialty | Hematology and oncology |
| Causes | Idiopathic; HIV; Epstein-Barr Virus; MYC gene translocation |
| Differential diagnosis | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, high-grade B cell lymphoma, lymphoblastic leukemia, mantle cell lymphoma (blastoid variant) |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy |
Burkitt lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, particularly B lymphocytes found in the germinal center. It is named after Denis Parsons Burkitt, the Irish surgeon who first described the disease in 1958 while working in equatorial Africa.[1][2] It is a highly aggressive form of cancer which often, but not always, manifests after a person develops acquired immunodeficiency from infection with Epstein-Barr Virus or Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).[3][4]
The overall cure rate for Burkitt lymphoma in developed countries is about 90%. Burkitt lymphoma is uncommon in adults, in whom it has a worse prognosis.[5]
- ^ synd/2511 at Who Named It?
- ^ Burkitt D (1958). "A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children". The British Journal of Surgery. 46 (197): 218–23. doi:10.1002/bjs.18004619704. PMID 13628987. S2CID 46452308.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Roschewski 2022 NEJMwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Gonzales, Blanca; Wang, Luojun; Campo, Elias (2021). "Chapter 95: Pathology of Lymphomas". Williams Hematology (10th ed.). New York: McGraw Hill.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid22333947was invoked but never defined (see the help page).