
Back قشرة الخلية Arabic Kortikaalne tsütoplasma Estonian Cortex cellulaire French Stanični korteks Croatian Cortex cellulare Italian 細胞皮質 Japanese 细胞皮层 Chinese
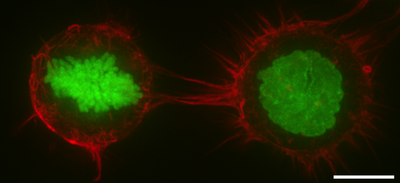
The cell cortex, also known as the actin cortex, cortical cytoskeleton or actomyosin cortex, is a specialized layer of cytoplasmic proteins on the inner face of the cell membrane. It functions as a modulator of membrane behavior and cell surface properties.[1][2][3] In most eukaryotic cells lacking a cell wall, the cortex is an actin-rich network consisting of F-actin filaments, myosin motors, and actin-binding proteins.[4][5] The actomyosin cortex is attached to the cell membrane via membrane-anchoring proteins called ERM proteins that plays a central role in cell shape control.[1][6] The protein constituents of the cortex undergo rapid turnover, making the cortex both mechanically rigid and highly plastic, two properties essential to its function. In most cases, the cortex is in the range of 100 to 1000 nanometers thick.
In some animal cells, the protein spectrin may be present in the cortex. Spectrin helps to create a network by cross-linked actin filaments.[3] The proportions of spectrin and actin vary with cell type.[7] Spectrin proteins and actin microfilaments are attached to transmembrane proteins by attachment proteins between them and the transmembrane proteins. The cell cortex is attached to the inner cytosolic face of the plasma membrane in cells where the spectrin proteins and actin microfilaments form a mesh-like structure that is continuously remodeled by polymerization, depolymerization and branching.
Many proteins are involved in the cortex regulation and dynamics, including formins, with roles in actin polymerization, Arp2/3 complexes that give rise to actin branching and capping proteins. Due to the branching process and the density of the actin cortex, the cortical cytoskeleton can comprise a highly complex meshwork such as a fractal structure.[8] Specialized cells are usually characterized by a very specific cortical actin cytoskeleton. For example, in red blood cells, the cell cortex consists of a two-dimensional cross-linked elastic network with pentagonal or hexagonal symmetry, tethered to the plasma membrane and formed primarily by spectrin, actin and ankyrin.[9] In neuronal axons, the actin or spectric cytoskeleton forms an array of periodic rings [10] and in the sperm flagellum it forms a helical structure.[11]
In plant cells, the cell cortex is reinforced by cortical microtubules underlying the plasma membrane. The direction of these cortical microtubules determines which way the cell elongates when it grows.
- ^ a b Salbreux G, Charras G, Paluch E (October 2012). "Actin cortex mechanics and cellular morphogenesis". Trends in Cell Biology. 22 (10): 536–45. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2012.07.001. PMID 22871642.
- ^ Pesen D, Hoh JH (January 2005). "Micromechanical architecture of the endothelial cell cortex". Biophysical Journal. 88 (1): 670–9. Bibcode:2005BpJ....88..670P. doi:10.1529/biophysj.104.049965. PMC 1305044. PMID 15489304.
- ^ a b Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter (2002). "Cross-linking Proteins with Distinct Properties Organize Different Assemblies of Actin Filaments". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). New York: Garland Science. ISBN 0-8153-3218-1.
- ^ Gunning PW, Ghoshdastider U, Whitaker S, Popp D, Robinson RC (June 2015). "The evolution of compositionally and functionally distinct actin filaments". Journal of Cell Science. 128 (11): 2009–19. doi:10.1242/jcs.165563. PMID 25788699.
- ^ Clark AG, Wartlick O, Salbreux G, Paluch EK (May 2014). "Stresses at the cell surface during animal cell morphogenesis". Current Biology. 24 (10): R484-94. Bibcode:2014CBio...24.R484C. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.059. PMID 24845681.
- ^ Fehon RG, McClatchey AI, Bretscher A (April 2010). "Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 11 (4): 276–87. doi:10.1038/nrm2866. PMC 2871950. PMID 20308985.
- ^ Machnicka B, Grochowalska R, Bogusławska DM, Sikorski AF, Lecomte MC (January 2012). "Spectrin-based skeleton as an actor in cell signaling". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 69 (2): 191–201. doi:10.1007/s00018-011-0804-5. PMC 3249148. PMID 21877118.
- ^ Sadegh S, Higgins JL, Mannion PC, Tamkun MM, Krapf D (2017). "Plasma Membrane is Compartmentalized by a Self-Similar Cortical Actin Meshwork". Physical Review X. 7 (1): 011031. arXiv:1702.03997. Bibcode:2017PhRvX...7a1031S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevX.7.011031. PMC 5500227. PMID 28690919.
- ^ Gov NS (January 2007). "Active elastic network: cytoskeleton of the red blood cell". Physical Review E. 75 (1 Pt 1): 011921. Bibcode:2007PhRvE..75a1921G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.75.011921. PMID 17358198.
- ^ Xu K, Zhong G, Zhuang X (January 2013). "Actin, spectrin, and associated proteins form a periodic cytoskeletal structure in axons". Science. 339 (6118): 452–6. Bibcode:2013Sci...339..452X. doi:10.1126/science.1232251. PMC 3815867. PMID 23239625.
- ^ Gervasi MG, Xu X, Carbajal-Gonzalez B, Buffone MG, Visconti PE, Krapf D (June 2018). "The actin cytoskeleton of the mouse sperm flagellum is organized in a helical structure". Journal of Cell Science. 131 (11): jcs215897. doi:10.1242/jcs.215897. PMC 6031324. PMID 29739876.