| Central nucleus of the amygdala | |
|---|---|
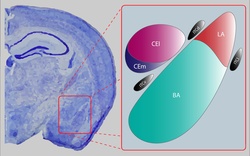 | |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2682 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA or aCeN) is a nucleus within the amygdala.[1][2] It "serves as the major output nucleus of the amygdala and participates in receiving and processing pain information."[3][4][5][6]
CeA "connects with brainstem areas that control the expression of innate behaviors and associated physiological responses."[7]
CeA is responsible for "autonomic components of emotions (e.g., changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration) primarily through output pathways to the lateral hypothalamus and brain stem." The CeA is also responsible for "conscious perception of emotion primarily through the ventral amygdalofugal output pathway to the anterior cingulate cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, and prefrontal cortex."[8]
- ^ Keifer OP, Hurt RC, Ressler KJ, Marvar PJ (September 2015). "The Physiology of Fear: Reconceptualizing the Role of the Central Amygdala in Fear Learning". Physiology. 30 (5): 389–401. doi:10.1152/physiol.00058.2014. PMC 4556826. PMID 26328883.
- ^ Kalin NH, Shelton SE, Davidson RJ (June 2004). "The role of the central nucleus of the amygdala in mediating fear and anxiety in the primate". The Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (24): 5506–5515. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0292-04.2004. PMC 6729317. PMID 15201323.
- ^ Companion MA, Gonzalez DA, Robinson SL, Herman MA, Thiele TE (2022-09-01). "Lateral habenula-projecting central amygdala circuits expressing GABA and NPY Y1 receptor modulate binge-like ethanol intake in mice". Addiction Neuroscience. 3: 100019. doi:10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100019. ISSN 2772-3925. PMC 9435303. PMID 36059430. S2CID 248484807.
- ^ Roberto M, Gilpin NW, Siggins GR (December 2012). "The central amygdala and alcohol: role of γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and neuropeptides". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine. 2 (12): a012195. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a012195. PMC 3543070. PMID 23085848.
- ^ Swanson LW, Petrovich GD (August 1998). "What is the amygdala?". Trends in Neurosciences. 21 (8): 323–331. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(98)01265-X. PMID 9720596. S2CID 11826564.
- ^ Hasanein P, Mirazi N, Javanmardi K (November 2008). "GABAA receptors in the central nucleus of amygdala (CeA) affect on pain modulation". Brain Research. 1241: 36–41. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.09.041. PMID 18838064. S2CID 46000492.
- ^ LeDoux JE (2008). "Amygdala". Scholarpedia. 3 (4): 2698. Bibcode:2008SchpJ...3.2698L. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.2698.
- ^ Wright A. "Limbic System: Amygdala". In Byrne JH (ed.). Homeostasis and Higher Brain Function. Neuroscience Online. University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. Archived from the original on 2013-11-07. Retrieved 2013-02-14.
