
Back Llingües chukoto-kamchatka AST Çukot-kamçat dilləri Azerbaijani چوکوت-کامچات دیللری AZB Čiokčiu-kamčiadalu kalbas BAT-SMG Llengües txukotkokamtxatkianes Catalan Čukotsko-kamčatské jazyky Czech Tschuktscho-kamtschadalische Sprachen German Ĉukĉa-kamĉatka lingvaro Esperanto Lenguas chukoto-kamchatka Spanish Tšuktši-kamtšadali keeled Estonian
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2021) |
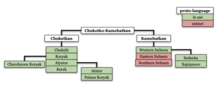
| Chukotko-Kamchatkan | |
|---|---|
| Chukchi–Kamchatkan, Luorawetlan | |
| Geographic distribution | Russian Far East |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Chukotko-Kamchatkan |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | chuk1271 |
 The distribution of Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages (red) in the 17th century (hatching, approximate) and at the end of the 20th century (solid). | |
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan or Chukchi–Kamchatkan languages are a language family of extreme northeastern Siberia. Its speakers traditionally were indigenous hunter-gatherers and reindeer-herders. Chukotko-Kamchatkan is endangered. The Kamchatkan branch is moribund, represented only by Western Itelmen, with less than a hundred speakers left.[1] The Chukotkan branch had close to 7,000 speakers left (as of 2010, the majority being speakers of Chukchi), with a reported total ethnic population of 25,000.[2]
While the family is sometimes grouped typologically and geographically as Paleosiberian, no external genetic relationship has been widely accepted as proven. The most popular such proposals have been for links with Eskimo–Aleut, either alone or in the context of a wider grouping.
- ^ "Russian National Census". Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 27 August 2024.
- ^ Russian Census (2010); see also Demographics of Siberia.