
Back Cultura de Cishan Catalan Cishan-Kultur German Culture de Cishan French Cesan-kultúra Hungarian Cultura di Cishan Italian 磁山文化 Japanese 츠산 문화 Korean Cishancultuur Dutch Kultura Cishan Polish Văn hóa Từ Sơn Vietnamese
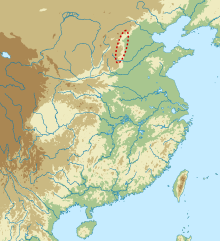 | |||||||
| Geographical range | Hebei, Henan | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Neolithic China | ||||||
| Dates | 6500–5000 BC | ||||||
| Type site | Cishan | ||||||
| Preceded by | Nanzhuangtou | ||||||
| Followed by | Yangshao culture | ||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Chinese | 磁山文化 | ||||||
| |||||||
36°42′N 114°12′E / 36.7°N 114.2°E
The Cishan culture (6500–5000 BC) was a Neolithic culture in northern China, on the eastern foothills of the Taihang Mountains.[1] The Cishan culture was based on the farming of broomcorn millet, the cultivation of which on one site has been dated back 10,000 years.[2] The people at Cishan also began to cultivate foxtail millet around 8700 years ago.[3] However, these early dates have been questioned by some archaeologists due to sampling issues and lack of systematic surveying.[4]
Common artifacts from the Cishan culture include stone grinders, stone sickles and tripod pottery. The sickle blades feature fairly uniform serrations, which made the harvesting of grain easier. Cord markings, used as decorations on the pottery, was more common compared to neighboring cultures. Also, the Cishan potters created a broader variety of pottery forms such as basins, pot supports, serving stands, and drinking cups.
Since the culture shared many similarities with its southern neighbor, the Peiligang culture, both cultures were sometimes previously referred to together as the Cishan-Peiligang culture or Peiligang-Cishan culture. The Cishan culture also shared several similarities with its eastern neighbor, the Beixin culture. However, the contemporary consensus among archaeologists is that the Cishan people were members of a distinct culture that shared many characteristics with its neighbors.[5]
This culture has been linked to the origin of the Sino-Tibetan language family.[6]

- ^ Liu & Chen 2012, p. 133.
- ^ Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K. -B.; Wu, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Ye, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Shen, L.; Xu, D.; Li, Q. (2009). "Earliest domestication of common millet (Panicum miliaceum) in East Asia extended to 10,000 years ago". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106 (18): 7367–7372. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106.7367L. doi:10.1073/pnas.0900158106. PMC 2678631. PMID 19383791.
- ^ Liu & Chen 2012, p. 84.
- ^ Liu & Chen 2012, pp. 84, 133–134.
- ^ Zhu 2013.
- ^ a b Sagart et al. (2019), pp. 10319–10320.