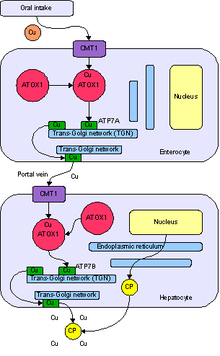
Copper is an essential trace element that is vital to the health of all living things (plants, animals and microorganisms). In humans, copper is essential to the proper functioning of organs and metabolic processes. Also, in humans, copper helps maintain the nervous system, immune system, brain development, and activates genes, as well as assisting in the production of connective tissues, blood vessels, and energy.[1] The human body has complex homeostatic mechanisms which attempt to ensure a constant supply of available copper, while eliminating excess copper whenever this occurs. However, like all essential elements and nutrients, too much or too little nutritional ingestion of copper can result in a corresponding condition of copper excess or deficiency in the body, each of which has its own unique set of adverse health effects.
Daily dietary standards for copper have been set by various health agencies around the world. Standards adopted by some nations recommend different copper intake levels for adults, pregnant women, infants, and children, corresponding to the varying need for copper during different stages of life.
- ^ "Copper - Fact sheet for consumers". National Institutes of Health.
