
Back Aweueh ACE Koljander Afrikaans ድምብላል Amharic Coriandrum sativum AN كزبرة Arabic كزبره ARZ ধনিয়া Assamese Coriandrum sativum AST Əkin keşnişi Azerbaijani گشنیز AZB
| Coriander or cilantro | |
|---|---|
| |
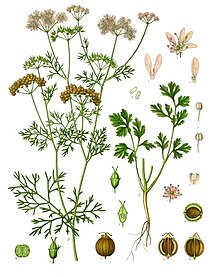
| Illustration of coriander parts | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Coriandrum |
| Species: | C. sativum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Coriandrum sativum | |
Coriander (/ˌkɒriˈændər, ˈkɒriændər/;[1] Coriandrum sativum), also known as cilantro (/sɪˈlæntroʊ, -ˈlɑːn-/),[1]: 90 is an annual herb in the family Apiaceae.
Most people perceive coriander to have a tart, slightly citrus taste. Due to variations in the gene OR6A2, some people perceive it to have a soap-like taste, or even a pungent or rotten taste.[2]
It is native to the Mediterranean Basin.[3] All parts of the plant are edible, but the fresh leaves and the dried seeds are the parts most traditionally used in cooking.
- ^ a b Jones D (6 October 2011). Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary. Cambridge University Press. p. 110. ISBN 978-0-521-76575-6. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ Eriksson N, Wu S, Do C (29 November 2012). "A genetic variant near olfactory receptor genes influences cilantro preference". Flavour. 1. arXiv:1209.2096. doi:10.1186/2044-7248-1-22. S2CID 199627.
- ^ Grivetti L. "Coriander". Nutritional Geography: The integration of physical landscape, culture, and economics. University of California, Davis Nutrition Department. Retrieved 7 December 2023.