
Back إنضار Arabic Debridement Azerbaijani Débridement German Desbridamiento Spanish دبریدمان Persian Parage (médecine) French הטריה HE Sbrigliamento Italian デブリードマン Japanese Сауықтыру Kazakh
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2013) |
| Debridement | |
|---|---|
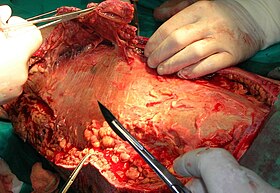 Necrotic tissue from the left leg is being surgically debrided in a patient with necrotizing fasciitis. | |
| Pronunciation | /dɪˈbriːdmənt/[1] |
| ICD-10-PCS | 0?D |
| MeSH | D003646 |
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue.[2][3] Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), or by maggot therapy.
In podiatry, practitioners such as chiropodists, podiatrists and foot health practitioners remove conditions such as calluses and verrucas.
Debridement is an important part of the healing process for burns and other serious wounds; it is also used for treating some kinds of snake and spider bites.
Sometimes the boundaries of the problem tissue may not be clearly defined. For example, when excising a tumor, there may be micrometastases along the edges of the tumor that are too small to be detected, but if not removed, could cause a relapse. In such circumstances, a surgeon may opt to debride a portion of the surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that the tumor is completely removed.
- ^ "Merriam-Webster Dictionary". merriam-webster.com. 27 May 2024.
- ^ "debridement". merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 5 September 2013.
- ^ "Understand Debridement Before You Regret – Why you Need Debridement". HealthNmedicarE. 24 March 2018. Archived from the original on 9 April 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2018.