
Back Spike (Beugung) German Aigrettes de diffraction French Difrakcinės smailės Lithuanian Дифракционные лучи Russian

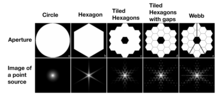
Diffraction spikes are lines radiating from bright light sources, causing what is known as the starburst effect[1] or sunstars[2] in photographs and in vision. They are artifacts caused by light diffracting around the support vanes of the secondary mirror in reflecting telescopes, or edges of non-circular camera apertures, and around eyelashes and eyelids in the eye.
While similar in appearance, this is a different effect to "vertical smear" or "blooming" that appears when bright light sources are captured by a charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensor.
- ^ Cheong, Kang Hao; Koh, Jin Ming; Tan, Joel Shi Quan; Lendermann, Markus (2018-11-16). "Computational Imaging Prediction of Starburst-Effect Diffraction Spikes". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 16919. Bibcode:2018NatSR...816919L. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-34400-z. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 6240111. PMID 30446668.
- ^ Brockway, Don (November 1989). "Scenics". Popular Photography: 55.