
Back Dimethylheptylpyran German Dimetilheptilpirano Spanish Dimetyyliheptyylipyraani Finnish Diméthylheptylpyrane French Dimetyloheptylopiran Polish Dimetilheptilpiran Serbo-Croatian Dimetilheptilpiran Serbian
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 20–39 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
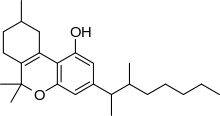
| Formula | C25H38O2 |
| Molar mass | 370.577 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dimethylheptylpyran (DMHP, 3-(1,2-dimethylheptyl)-Δ6a(10a)-THC, 1,2-dimethylheptyl-Δ3-THC, A-40824, or EA-2233) is a synthetic analog of THC, which was invented in 1949 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of Cannabis.[2] DMHP is a pale yellow, viscous oil which is insoluble in water but dissolves in alcohol or non-polar solvents.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-07-24). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-07-25). Archived from the original on 2023-08-27. Retrieved 2023-08-27.
- ^ Adams R, Harfenist M, Loewe S (1949). "New Analogs of Tetrahydrocannabinol. XIX". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 71 (5): 1624–1628. doi:10.1021/ja01173a023.