
Back Nanolitografia dip-pen Catalan Nanolitografía dip-pen Spanish Teraviknanolitograafia Estonian ננוליתוגרפיית עט נובע HE
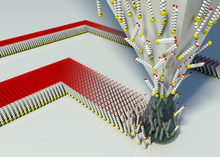
Dip pen nanolithography (DPN) is a scanning probe lithography technique where an atomic force microscope (AFM) tip is used to directly create patterns on a substrate.[1] It can be done on a range of substances with a variety of inks. A common example of this technique is exemplified by the use of alkane thiolates to imprint onto a gold surface.[2] This technique allows surface patterning on scales of under 100 nanometers. DPN is the nanotechnology analog of the dip pen (also called the quill pen), where the tip of an atomic force microscope cantilever acts as a "pen", which is coated with a chemical compound or mixture acting as an "ink", and put in contact with a substrate, the "paper".[3]
DPN enables direct deposition of nanoscale materials onto a substrate in a flexible manner. Recent advances have demonstrated massively parallel patterning using two-dimensional arrays of 55,000 tips.
Applications of this technology currently range through chemistry, materials science, and the life sciences, and include such work as ultra high density biological nanoarrays, and additive photomask repair.[4]
- ^ Ginger, David S.; Zhang, Hua; Mirkin, Chad A. (2004). "The Evolution of Dip-Pen Nanolithography". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 43 (1): 30–45. doi:10.1002/anie.200300608. ISSN 1433-7851. PMID 14694469.
- ^ Piner, R. D. (1999). ""Dip-Pen" Nanolithography". Science. 283 (5402): 661–663. doi:10.1126/science.283.5402.661. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9924019. S2CID 27011581.
- ^ "DPN – Northwestern – Intro". Northwestern University. Archived from the original on 12 June 2013. Retrieved 7 May 2013.
- ^ Elhadj, Selim; Chernov, Alexander A; De Yoreo, James J (13 February 2008). "Solvent-mediated repair and patterning of surfaces by AFM". Nanotechnology. 19 (10). IOP Publishing: 105304. Bibcode:2008Nanot..19j5304E. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/19/10/105304. ISSN 0957-4484. PMID 21817697. S2CID 22708216.