
Back خلل التنسج Arabic Displazija BS Displàsia Catalan Dysplazie Czech Dysplasi Danish Dysplasie German Displasia Spanish Düsplaasia Estonian دیسپلازی Persian Dysplasia Finnish

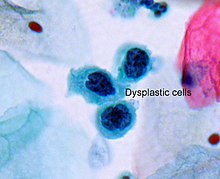
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth.[1] Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney.
In one of the modern histopathological senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not cancerous. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus cover a spectrum of histopathological variations.
- ^ "Definition of dysplasia". Merriam-Webster dictionary. Retrieved 2019-09-09.