
Back Llingües indoaries orientales AST पुरबी इंडो-आर्यन भाषा Bihari পূর্ব ইন্দো-আর্য ভাষা Bengali/Bangla Lenguas indoarias orientales Spanish 동인도아리아어군 Korean Fiteny indô-ariàna atsinanana Malagasy पूर्वी आर्य भाषा परिवार Nepali Lengas indoarianas de l'èst Occitan पूर्वहिन्द-आर्यभाषाः Sanskrit
| Eastern Indo-Aryan | |
|---|---|
| Magadhan | |
| Geographic distribution | Eastern India, Bangladesh, southern Nepal |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
Early forms | |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | indo1323 (Indo-Aryan Eastern zone)biha1245 (Bihari) |
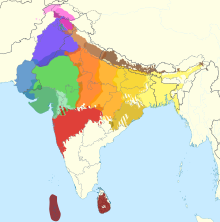
The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Māgadhan languages, are spoken throughout the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, which includes Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bengal region, Tripura, Assam, and Odisha; alongside other regions surrounding the northeastern Himalayan corridor. Bengali is official language of Bangladesh and the state of West Bengal, Tripura and the Barak valley of Assam while Assamese and Odia are the official languages of Assam and Odisha, respectively. The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Abahattha, which descends from Magadhan Apabhraṃśa[1] and ultimately from Magadhi Prakrit.[2][3][1]
- ^ a b Ray, Tapas S. (2007). "Chapter Eleven: "Oriya". In Jain, Danesh; Cardona, George. The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. p. 445. ISBN 978-1-135-79711-9.
- ^ Cardona, George; Jain, Dhanesh, eds. (2003), "The historical context and development of Indo-Aryan", The Indo-Aryan Languages, Routledge language family series, London: Routledge, pp. 46–66, ISBN 0-7007-1130-9
- ^ South Asian folklore: an encyclopedia : Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, By Peter J. Claus, Sarah Diamond, Margaret Ann Mills, Routledge, 2003, p. 203