| History of Indonesia |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
|
|
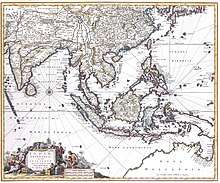
The economic history of Indonesia is shaped by its geographic location, its natural resources, as well as its people that inhabited the archipelago that today formed the modern nation-state of the Republic of Indonesia. The foreign contact and international trade with foreign counterparts had also shaped and sealed the fate of Indonesian archipelago, as Indians, Chinese, Arabs, and eventually European traders reached the archipelago during the Age of Exploration and participated in the spice trade, war and conquest.
By the early 17th century, the Dutch East India Company (VOC), one of the world's earliest multinational companies, had established their base in the archipelago as they monopolised the spice trade. By 1800, the Dutch East Indies colonial state had emerged and benefited from cash crop trades of coffee, tea, quinine, rubber and palm oil from the colony, also from the mining sector: oil, coal, tin and copper. The colonial state would be succeeded by the Indonesian Republic after World War II.
By the early 21st century, Indonesia rose to be the largest economy in Southeast Asia, as one of the emerging market economies of the world, a member of G-20 major economies and classified as a newly industrialised country.[1]
- ^ "About the G20". G20.
