
Back تطور الحيتانيات Arabic Evolució dels cetacis Catalan پەرەسەندنی نەھەنگەکان CKB Evolución de los cetáceos Spanish فرگشت آببازسانان Persian Valaiden evoluutio Finnish Histoire évolutive des cétacés French אבולוציה של לווייתנאים HE A cetek evolúciója Hungarian Evolusi Cetacea ID

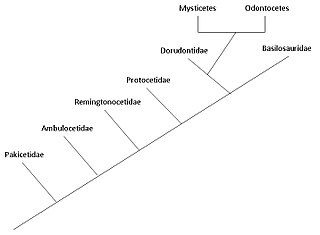
The evolution of cetaceans is thought to have begun in the Indian subcontinent from even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla) 50 million years ago (mya) and to have proceeded over a period of at least 15 million years.[2] Cetaceans are fully aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla and branched off from other artiodactyls around 50 mya. Cetaceans are thought to have evolved during the Eocene (56-34 mya), the second epoch of the present-extending Cenozoic Era. Molecular and morphological analyses suggest Cetacea share a relatively recent closest common ancestor with hippopotami and that they are sister groups.[3] Being mammals, they surface to breathe air; they have five finger bones (even-toed) in their fins; they nurse their young; and, despite their fully aquatic life style, they retain many skeletal features from their terrestrial ancestors.[4][5] Research conducted in the late 1970s in Pakistan revealed several stages in the transition of cetaceans from land to sea.
The two modern parvorders of cetaceans – Mysticeti (baleen whales) and Odontoceti (toothed whales) – are thought to have separated from each other around 28–33 mya in a second cetacean radiation, the first occurring with the archaeocetes.[6] The adaptation of animal echolocation in toothed whales distinguishes them from fully aquatic archaeocetes and early baleen whales. The presence of baleen in baleen whales occurred gradually, with earlier varieties having very little baleen, and their size is linked to baleen dependence (and subsequent increase in filter feeding).
- ^ Thewissen, J. G. M.; Williams, E. M. (1 November 2002). "The Early Radiation of Cetacea (Mammalia): Evolutionary Pattern and Developmental Correlations". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 33 (1): 73–90. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.020602.095426.
- ^ Davis, R. W. 2019. Return to the Sea: The Evolution of Marine Mammals. Pages 7–27 in R. W. Davis, ed. Marine Mammals: Adaptations for an Aquatic Life. Springer International Publishing, New York.
- ^ Geisler, J. H., and M. D. Uhen. 2005. Phylogenetic relationships of extinct Cetartiodactyls: results of simultaneous analyses of molecular, morphological, and stratigraphic data. Journal of Mammalian Evolution 12:145–160.
- ^ Berta, A., J. L. Sumich, and K. M. Kovacs. 2005. Marine Mammals: Evolutionary Biology. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
- ^ Thewissen, J. G. M., L. N. Cooper, J. C. George, and S. Bajpai. 2009. From land to water: the origin of whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Evolution: Education and Outreach 2:272–288.
- ^ Nikaido, M.; Matsuno, F. (2001). "Retroposon analysis of major cetacean lineages: The monophyly of toothed whales and the paraphyly of river dolphins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 98 (13): 7384–9. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.7384N. doi:10.1073/pnas.121139198. PMC 34678. PMID 11416211.