
Back إسقاط فيشر Arabic Проекция на Фишер Bulgarian ফিশার অভিক্ষেপ Bengali/Bangla Projecció de Fischer Catalan Fischerova projekce Czech Fischer-Projektion German Proyección de Fischer Spanish Fischerin projektio Finnish Projection de Fischer French Teilgean Fischer Irish
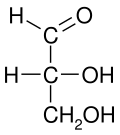
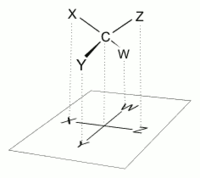

In chemistry, the Fischer projection, devised by Emil Fischer in 1891, is a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional organic molecule by projection. Fischer projections were originally proposed for the depiction of carbohydrates and used by chemists, particularly in organic chemistry and biochemistry. The use of Fischer projections in non-carbohydrates is discouraged, as such drawings are ambiguous and easily confused with other types of drawing. The main purpose of Fischer projections is to show the chirality of a molecule and to distinguish between a pair of enantiomers. Some notable uses include drawing sugars and depicting isomers.[1]
- ^ Gregersen E. "Fischer Projection | Definition & Facts". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2022-11-17.