Back Furaan Afrikaans فوران (مركب كيميائي) Arabic Furan Azerbaijani فوران AZB Фуран Byelorussian Фуран Bulgarian Furan BS Furan Catalan Furan Czech Furan German
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Furan[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,4-Epoxybuta-1,3-diene 1-Oxacyclopenta-2,4-diene | |||
| Other names
Oxole
Oxa[5]annulene 1,4-Epoxy-1,3-butadiene 5-Oxacyclopenta-1,3-diene 5-Oxacyclo-1,3-pentadiene Furfuran Divinylene oxide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 103221 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.390 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 25716 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2389 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4O | |||
| Molar mass | 68.075 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, volatile liquid | ||
| Density | 0.936 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −85.6 °C (−122.1 °F; 187.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 31.3 °C (88.3 °F; 304.4 K) | ||
| -43.09·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H224, H302, H315, H332, H341, H350, H373, H412 | |||
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P314, P321, P330, P332+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −36 °C (−33 °F; 237 K) | ||
| 390 °C (734 °F; 663 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | Lower: 2.3% Upper: 14.3% at 20 °C | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
> 2 g/kg (rat) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Pennakem | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related heterocycles
|
Pyrrole Thiophene | ||
Related compounds
|
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) 2,5-Dimethylfuran Benzofuran Dibenzofuran | ||
| Structure | |||
| C2v | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
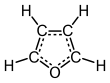
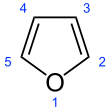
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
Furan is a colorless, flammable, highly volatile liquid with a boiling point close to room temperature. It is soluble in common organic solvents, including alcohol, ether, and acetone, and is slightly soluble in water.[2] Its odor is "strong, ethereal; chloroform-like".[3] It is toxic and may be carcinogenic in humans. Furan is used as a starting point for other speciality chemicals.[4]
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 392. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Jakubke, Hans Dieter; Jeschkeit, Hans (1994). Concise Encyclopedia of Chemistry. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1–1201. ISBN 0-89925-457-8.
- ^ DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2016–171, p. 2, Accessed Nov 2019
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).