
Back Cheografía d'Alcheria AN جغرافيا الجزائر Arabic Xeografía d'Arxelia AST География на Алжир Bulgarian আলজেরিয়ার ভূগোল Bengali/Bangla Geografia d'Algèria Catalan Γεωγραφία της Αλγερίας Greek Geografio de Alĝerio Esperanto Geografía de Argelia Spanish Aljeriako geografia Basque
  | |
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Region | North Africa |
| Coordinates | 28°00′N 3°00′E / 28.000°N 3.000°E |
| Area | Ranked 10th |
| • Total | 2,381,741 km2 (919,595 sq mi) |
| • Land | 100% |
| • Water | 0% |
| Coastline | 2,148 km (1,335 mi) |
| Borders | Land boundaries: 6,343 km Morocco 1,559 km, Mali 1,376 km, Libya 982 km, Tunisia 965 km, Niger 956 km, Mauritania 463 km, Western Sahara 42 km |
| Maritime claims | 32–52 nm |
| Highest point | Mount Tahat, 3,003 m |
| Lowest point | Chott Melrhir, −40 m (131 ft) |
| Longest river | Chelif River, 230 km |
| Climate | arid to semiarid |
| Terrain | mostly high plateau and desert, mountains, narrow coastal plain[1] |
| Natural resources | petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, uranium, lead, zinc[1] |
| Natural hazards | earthquakes, mudslides, floods, droughts |
| Environmental issues | soil erosion, desertification, pollution |
| Exclusive economic zone | 126,353 km2 (48,785 sq mi) |


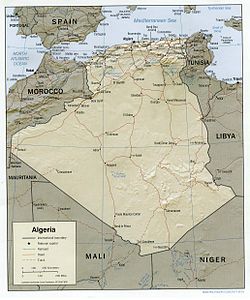
Algeria comprises 2,381,740 square kilometres (919,590 sq mi) of land, more than 80% of which is desert, in North Africa, between Morocco and Tunisia.[2][1] It is the largest country in Africa.[1] Its Arabic name, Al Jazair (the islands), is believed to derive from the rocky islands along the coastline of the Mediterranean Sea.[2] The northern portion, an area of mountains, valleys, and plateaus between the Mediterranean and the Sahara Desert, forms an integral part of the section of North Africa known as the Maghreb.[2] This area includes Morocco, Tunisia, and the northwestern portion of Libya known historically as Tripolitania.[2]
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
factbookwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Deeb, Mary-Jane (1993). "Physical Setting". In Metz, Helen Chapin (ed.). Algeria: a country study. Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 69–76. OCLC 44230753.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)