
Back هجوم الربيع Arabic Вясновае наступленне (1918) Byelorussian Пролетно настъпление Bulgarian বসন্ত আক্রমণ Bengali/Bangla Argadenn an Nevezhañv Breton Ofensiva de primavera Catalan Ludendorffova ofenzíva Czech Den tyske forårsoffensiv 1918 Danish Deutsche Frühjahrsoffensive 1918 German Kaiserschlacht Spanish
| German spring offensive | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Western Front of World War I | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
The German spring offensive, also known as Kaiserschlacht ("Kaiser's Battle") or the Ludendorff offensive, was a series of German attacks along the Western Front during the First World War, beginning on 21 March 1918. Following American entry into the war in April 1917, the Germans decided that their only remaining chance of victory was to defeat the Allies before the United States could ship soldiers across the Atlantic and fully deploy its resources. The German Army had gained a temporary advantage in numbers as nearly 50 divisions had been freed by the Russian defeat and withdrawal from the war with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.
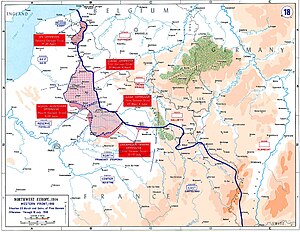
There were four German offensives, codenamed Michael, Georgette, Gneisenau, and Blücher-Yorck. Michael was the main attack, which was intended to break through the Allied lines, outflank the British forces (which held the front from the Somme River to the English Channel) and defeat the British Army. Once that was achieved, it was hoped that the French would seek armistice terms. The other offensives were subsidiary to Michael and were designed to divert Allied forces from the main offensive effort on the Somme. No clear objective was established before the start of the offensives and once the operations were underway, the targets of the attacks were constantly changed, depending on the tactical situation.
Once they began advancing, the Germans struggled to maintain the momentum, partly due to logistical issues. The fast-moving stormtrooper units could not carry enough food and ammunition to sustain themselves for long, and the army could not move in supplies and reinforcements fast enough to assist them. The Allies concentrated their main forces in the essential areas (the approaches to the Channel Ports and the rail junction of Amiens). Strategically worthless ground, which had been devastated by years of conflict, was left lightly defended. Within a few weeks, the danger of a German breakthrough had passed, though related fighting continued until July.
The German Army made the deepest advances either side had made on the Western Front since 1914. They re-took much ground that they had lost in 1916–17 and took some ground that they had not yet controlled. Despite these apparent successes, they suffered heavy casualties in return for land that was of little strategic value and hard to defend. The offensive failed to deliver a blow that could save Germany from defeat, which has led some historians[who?] to describe it as a Pyrrhic victory. In July 1918, the Allies regained their numerical advantage with the arrival of American troops. In August, they used this and improved tactics to launch a counteroffensive. The ensuing Hundred Days Offensive resulted in the Germans losing all of the ground that they had taken in the Spring Offensive, the collapse of the Hindenburg Line, and the capitulation of Germany that November.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Churchill, "The World Crisis, Vol. 2", p.963. German casualties from "Reichsarchiv 1918"
- ^ Churchill, "The World Crisis, Vol. 2", p.963. French casualties from "Official Returns to the Chamber, March 29, 1922"
- ^ Churchill, "The World Crisis, Vol. 2", p.963. British casualties from "Military Effort of the British Empire"
- ^ Edmonds, Davies & Maxwell-Hyslop 1995, pp. 147–148, 168.
- ^ "Le souvenir de la 1ère GM en Champagne-Ardenne – Le cimetière italien de Bligny présenté par Jean-Pierre Husson". www.cndp.fr. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2018.