
Back غليكوز أمينوغليكان Arabic Qlikozaminoqlikanlar Azerbaijani Glicosaminoglicà Catalan Glykosaminoglykane German Γλυκοζαμινογλυκάνες Greek Glicosoaminoglicano Spanish Glikosaminglukano Basque گلیکوزآمینوگلیکان Persian Glykosaminoglykaani Finnish Glycosaminoglycane French
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (July 2015) |
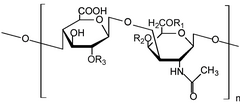
Glycosaminoglycans[1] (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides[2] are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit.[3] GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria.[4] Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers.
Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies.
- ^ "glycosaminoglycan" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ "mucopolysaccharide" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Esko, Jeffrey D; Kimata, Koji; Lindahl, Ulf (2009). "Chapter 16: Proteoglycans and Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans". Essentials of Glycobiology. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. ISBN 978-0879695590.
- ^ DeAngelis, Paul L. (2002-11-01). "Evolution of glycosaminoglycans and their glycosyltransferases: Implications for the extracellular matrices of animals and the capsules of pathogenic bacteria". The Anatomical Record. 268 (3): 317–326. doi:10.1002/ar.10163. ISSN 0003-276X. PMID 12382327. S2CID 38827411.