
Back ታላቅ ክብ Amharic دائرة عظمى Arabic Gran círculu AST Ҙур түңәрәк Bashkir Голяма окръжност Bulgarian মহাবৃত্ত Bengali/Bangla Kelc'h bras Breton Cercle màxim Catalan Hlavní kružnice Czech Storcirkel Danish
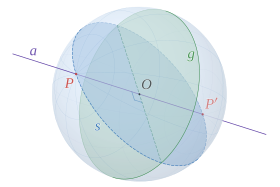

In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.[1][2]
- ^ W., Weisstein, Eric. "Great Circle -- from Wolfram MathWorld". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2022-09-30.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Weintrit, Adam; Kopcz, Piotr (2014). Loxodrome (Rhumb Line), Orthodrome (Great Circle), Great Ellipse and Geodetic Line (Geodesic) in Navigation. USA: CRC Press, Inc. ISBN 978-1-138-00004-9.