
Back هيميسليلوز Arabic হেমিসেলুলোজ Bengali/Bangla Hemiceluloza BS Hemicel·lulosa Catalan Hemicelulóza Czech Hemicellulose Danish Hemicellulose German Ημικυτταρίνες Greek Hemicelulosa Spanish Hemitselluloos Estonian
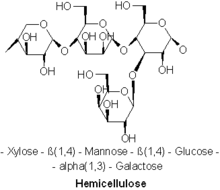
A hemicellulose (also known as polyose) is one of a number of heteropolymers (matrix polysaccharides), such as arabinoxylans, present along with cellulose in almost all terrestrial plant cell walls.[1] Cellulose is crystalline, strong, and resistant to hydrolysis. Hemicelluloses are branched, shorter in length than cellulose, and also show a propensity to crystallize.[2] They can be hydrolyzed by dilute acid or base as well as a myriad of hemicellulase enzymes.
- ^ Scheller HV, Ulvskov P.Hemicelluloses. // Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:263-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112315.
- ^ Smith, Peter J.; Curry, Thomas M.; Yang, Jeong-Yeh; Barnes, William J.; Ziegler, Samantha J.; Mittal, Ashutosh; Moremen, Kelley W.; York, William S.; Bomble, Yannick J.; Peña, Maria J.; Urbanowicz, Breeanna R. (2022-07-13). "Enzymatic Synthesis of Xylan Microparticles with Tunable Morphologies". ACS Materials Au. 2 (4): 440–452. doi:10.1021/acsmaterialsau.2c00006. ISSN 2694-2461. PMC 9284610. PMID 35856073.