
Back Автомагистрали в Полша Bulgarian Dálnice a rychlostní silnice v Polsku Czech Liste der Autobahnen und Schnellstraßen in Polen German Aŭtovojoj en Pollando Esperanto Puolan moottoritieverkko Finnish Liste des autoroutes de la Pologne French Lengyelország autópályái Hungarian Autostrade e superstrade in Polonia Italian アウトストラーダ (ポーランド) Japanese 아우토스트라다 (폴란드) Korean





Controlled-access highways in Poland are part of the national roads network and they are divided into motorways and expressways. Both types of highways feature grade-separated interchanges with all other roads, emergency lanes, feeder lanes, wildlife crossings and dedicated roadside rest areas. Motorways differ from expressways in their technical parameters like designated speed, permitted road curvature, lane widths or minimal distances between interchanges. Moreover, expressways might have single-carriageway sections in case of low traffic densities (as of 2024, such sections constitute 3.5% of the highway network).
The development of modern highways began in the 1970s, but proceeded very slowly under the communist rule and for the first years afterwards: between 1970 and 2000 only 434 km of highways were constructed in total (5% of the planned network).[2] Further 1050 km (13% of the network) were opened from 2001 to 2010, followed by 2773 km (34% of the network) constructed between 2011 and 2020.[3] It is planned to open about 2600 km (about 32%) in the 2020s, while the last ca. 15% would be completed after 2030.[4]
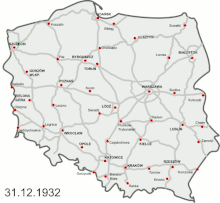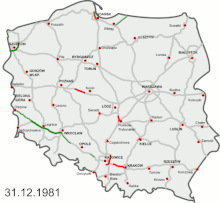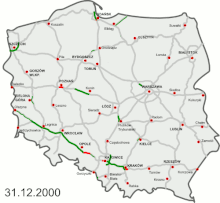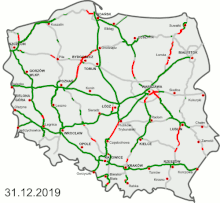
As of November 2024[update], there are 5173.4 km[5] of motorways and expressways in operation (62% of the intended network), while contracts for construction of further 1413 km[6][7] (17% of the network) are ongoing.
Except for the single-carriageway expressways, both types of highways fulfill the definition of a motorway as specified by OECD, WRA or Vienna Convention. Speed limits in Poland are 140 km/h on motorways and 120 km/h on expressways (100 km/h for single-carriageway expressway sections). Some motorway stretches are tolled.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ https://sip.lex.pl/akty-prawne/dzu-dziennik-ustaw/siec-autostrad-i-drog-ekspresowych-17100420
- ^ Here and in the following figures, construction of 1st or 2nd carriageway is accounted as half-length for consistency of the summed results. Sections constructed by Nazi Germany are accounted for the dates of their reconstruction to modern highways.
- ^ https://www.gov.pl/web/gddkia/mapa-stanu-budowy-drog4, more details: History
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pbdk_2033was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Autostrady :: Generalna Dyrekcja Dróg Krajowych i Autostrad - Strona Główna". www.gddkia.gov.pl.
- ^ Including design–build contracts; see the List of motorways and expressways for details on the phases of construction and design.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
gddkia_contracts'_completion_dateswas invoked but never defined (see the help page).