
Back Hidrogenering Afrikaans هدرجة Arabic Хидрогениране Bulgarian হাইড্রোজেনেশেন Bengali/Bangla Hidrogenacija BS Hidrogenació Catalan Hydrogenace Czech Hydrierung German Υδρογόνωση Greek Hidrogenación Spanish
| Hydrogenation | |
|---|---|
| Conditions | |
| Catalyst | Ni, Pd, Pt |
| Process type | Chemical |
|---|---|
| Industrial sector(s) | Food industry, petrochemical industry, pharmaceutical industry, agricultural industry |
| Main technologies or sub-processes | Various transition metal catalysts, high-pressure technology |
| Feedstock | Unsaturated substrates and hydrogen or hydrogen donors |
| Product(s) | Saturated hydrocarbons and derivatives |
| Inventor | Paul Sabatier |
| Year of invention | 1897 |
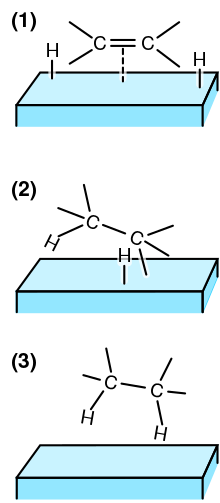
(1) The reactants are adsorbed on the catalyst surface and H2 dissociates.
(2) An H atom bonds to one C atom. The other C atom is still attached to the surface.
(3) A second C atom bonds to an H atom. The molecule leaves the surface.
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.[1]
- ^ Hudlický, Miloš (1996). Reductions in Organic Chemistry. Washington, D.C.: American Chemical Society. p. 429. ISBN 978-0-8412-3344-7.