Naval theatre of operations
 The pocket battleship Admiral Graf Spee brought World War II to the Indian Ocean in 1939.
The pocket battleship Admiral Graf Spee brought World War II to the Indian Ocean in 1939.
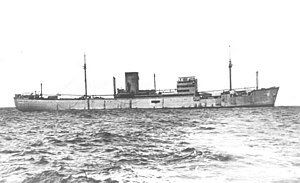 Atlantis was the first disguised commerce raider in the Indian Ocean.
Atlantis was the first disguised commerce raider in the Indian Ocean.
 Galileo Galilei was one of eight Italian submarines operating out of Massawa, and is shown here being captured by the Royal Navy.
Galileo Galilei was one of eight Italian submarines operating out of Massawa, and is shown here being captured by the Royal Navy.
 HMS Hermes as a convoy escort during the first year of wartime patrols.
HMS Hermes as a convoy escort during the first year of wartime patrols.
 Italian commerce raider Ramb I sinking.
Italian commerce raider Ramb I sinking.
 Fairey Albacore bombers launched from HMS Formidable raided Massawa.
Fairey Albacore bombers launched from HMS Formidable raided Massawa.
 Pantera was one of the destroyers based at Massawa destroyed when the Allies captured Italy's east African colonies.
Pantera was one of the destroyers based at Massawa destroyed when the Allies captured Italy's east African colonies.
 Commerce raider Kormoran preparing to refuel a U-boat.
Commerce raider Kormoran preparing to refuel a U-boat.
 HMAS Sydney was the only cruiser to be sunk by a commerce raider.
HMAS Sydney was the only cruiser to be sunk by a commerce raider.
 USS Langley under air attack south of Java.
USS Langley under air attack south of Java.
 HMAS Yarra was sunk by Japanese warships south of Java.
HMAS Yarra was sunk by Japanese warships south of Java.
 HMS Cornwall and HMS Dorsetshire under attack by Japanese dive bombers on 5 April 1942.
HMS Cornwall and HMS Dorsetshire under attack by Japanese dive bombers on 5 April 1942.
 HMS Cornwall sinking following air attack.
HMS Cornwall sinking following air attack.
 HMIS Indus in Akyab harbour, Burma, 1942.
HMIS Indus in Akyab harbour, Burma, 1942.
 Japanese submarine I-10 shown at Penang between Indian Ocean patrols.
Japanese submarine I-10 shown at Penang between Indian Ocean patrols.
 Bristol Blenheims of No. 60 Squadron RAF flying low to attack a Japanese coaster off Akyab, Burma on 11 October 1942.
Bristol Blenheims of No. 60 Squadron RAF flying low to attack a Japanese coaster off Akyab, Burma on 11 October 1942.
 Japanese commerce raider Hōkoku Maru.
Japanese commerce raider Hōkoku Maru.
 HMAS Arunta evacuated troops from Japanese-occupied Timor.
HMAS Arunta evacuated troops from Japanese-occupied Timor.
 Italy's most successful submarine Leonardo da Vinci sank ships in the western Indian Ocean during patrols from European bases.
Italy's most successful submarine Leonardo da Vinci sank ships in the western Indian Ocean during patrols from European bases.
 Dutch submarine O-21 patrolled the Andaman Sea.
Dutch submarine O-21 patrolled the Andaman Sea.
 Tenth Air Force B-24 Liberators sank several ships in the Andaman Sea.
Tenth Air Force B-24 Liberators sank several ships in the Andaman Sea.
 German submarine U-511 was the first U-boat to reach the eastern Indian Ocean and was presented to Japan as IJN RO-500.
German submarine U-511 was the first U-boat to reach the eastern Indian Ocean and was presented to Japan as IJN RO-500.
 HMS Tally-Ho was one of several British T-class submarines patrolling the Strait of Malacca.
HMS Tally-Ho was one of several British T-class submarines patrolling the Strait of Malacca.
 HMS Illustrious operated with USS Saratoga for Indian Ocean air raids.
HMS Illustrious operated with USS Saratoga for Indian Ocean air raids.
 HMS Khedive was one of several escort carriers serving in the Indian Ocean.
HMS Khedive was one of several escort carriers serving in the Indian Ocean.
 Fireflies returning to HMS Indefatigable following Operation Lentil airstrikes.
Fireflies returning to HMS Indefatigable following Operation Lentil airstrikes.
 Battleships HMS Valiant and Richelieu during Operation Bishop.
Battleships HMS Valiant and Richelieu during Operation Bishop.
 Operation Dracula was the last major amphibious landing in the Indian Ocean.
Operation Dracula was the last major amphibious landing in the Indian Ocean.
 German submarine U-532 was the last of the Monsun Gruppe to return to Europe, and is shown arriving in Liverpool after the German surrender.
German submarine U-532 was the last of the Monsun Gruppe to return to Europe, and is shown arriving in Liverpool after the German surrender.
 Haguro was sunk evacuating Japanese troops from Port Blair.
Haguro was sunk evacuating Japanese troops from Port Blair.
Prior to World War II, the Indian Ocean was an important maritime trade route between European nations and their colonial territories in East Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, British India, Indochina, the East Indies (Indonesia), and Australia for a long time. Naval presence was dominated by the Royal Navy Eastern Fleet and the Royal Australian Navy as World War II began, with a major portion of the Royal Netherlands Navy operating in the Dutch East Indies and the Red Sea Flotilla of the Italian Regia Marina operating from Massawa.
Axis naval forces gave a high priority to disrupting Allied trade in the Indian Ocean. Initial anti-shipping measures of unrestricted submarine warfare and covert raiding ships expanded to include airstrikes by aircraft carriers and raids by cruisers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. A Kriegsmarine Monsun Gruppe of U-boats operated from the eastern Indian Ocean after the Persian Corridor became an important military supply route to the Soviet Union.































