
Back أذن داخلية Arabic Daxili qulaq Azerbaijani Унутранае вуха Byelorussian অন্তঃকর্ণ Bengali/Bangla Unutrašnje uho BS Orella interna Catalan Y glust fewnol Welsh Innenohr German Έσω ους Greek Interna orelo Esperanto
| Inner ear | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Artery | Labyrinthine artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | auris interna |
| MeSH | D007758 |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.001 |
| TA2 | 6935 |
| FMA | 60909 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
 |
| This article is one of a series documenting the anatomy of the |
| Human ear |
|---|

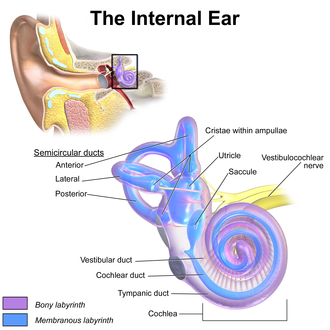
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance.[1] In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:[2]
- The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve.
- The vestibular system, dedicated to balance.
The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates.
- ^ Torres, M., Giráldez, F. (1998) The development of the vertebrate inner ear. Mechanisms of Development 71 (1–2) pp. 5–21
- ^ J.M. Wolfe et al. (2009). Sensation & Perception. 2nd ed. Sunderland: Sinauer Associated Inc