| Intermittent hypoxia | |
|---|---|
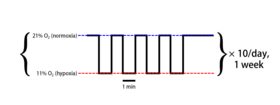 Example of a typical intermittent hypoxia protocol | |
| Other names | Episodic hypoxia |
Intermittent hypoxia (also known as episodic hypoxia) is an intervention in which a person or animal undergoes alternating periods of normoxia and hypoxia. Normoxia is defined as exposure to oxygen levels normally found in Earth's atmosphere (~21% O2) and hypoxia as any oxygen levels lower than those of normoxia. Normally, exposure to hypoxia is negatively associated to physiological changes to the body, such as altitude sickness.[1] However, when used in moderation, intermittent hypoxia may be used clinically as a means to alleviate various pathological conditions.[2]
