
Back Ioniese See Afrikaans Ionisches Meer ALS Mar Chonica AN البحر الأيوني Arabic Mar Xónicu AST İoni dənizi Azerbaijani یونان دنیزی AZB Ион диңгеҙе Bashkir Segara Ionia BAN Іанічнае мора Byelorussian
| Ionian Sea | |
|---|---|
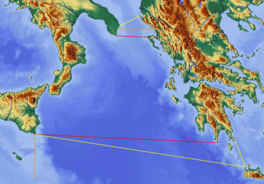 Boundaries of Ionian Sea: red lines define border per International Hydrographic Organization | |
| Location | Southern Europe |
| Coordinates | 38°N 19°E / 38°N 19°E |
| Type | Sea |
| Primary outflows | Mediterranean Sea |
| Basin countries | Albania, Greece, and Italy |
| Islands | List of islands in the Ionian Sea |
| Settlements | Igoumenitsa, Parga, Preveza, Astakos, Patras, Kerkyra, Lefkada, Argostoli, Zakynthos, Kyparissia, Pylos, Kalamata, Himarë, Sarandë, Syracuse, Catania, Taormina, Messina, Catanzaro, Crotone, Taranto |


The Ionian Sea (Modern Greek: Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, romanized: Iónio Pélagos, IPA: [iˈoni.o ˈpelaɣos];[a] Italian: Mar Ionio or Mar Jonio, IPA: [mar ˈjɔːnjo];[b] Albanian: Deti Jon, IPA: [ˈdɛti ˈjɔn]) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania (and western Apulia, Italy) to the north, and the west coast of Greece, including the Peloponnese.
All major islands in the sea, which are located in the east of the sea, belong to Greece. They are collectively named the Ionian Islands, the main ones being Corfu, Kefalonia, Zakynthos, Lefkada, and Ithaca.
There are ferry routes between Patras and Igoumenitsa, Greece, and Brindisi and Ancona, Italy, that cross the east and north of the Ionian Sea, and from Piraeus westward. Calypso Deep, the deepest point in the Mediterranean at 5,109 m (16,762 ft), is in the Ionian Sea, at 36°34′N 21°8′E / 36.567°N 21.133°E.[1][2] The sea is one of the most seismically active areas in the world.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Gade, Martin (March 15, 2008). "The European Marginal and Enclosed Seas: An Overview". In Barale, Vittorio (ed.). Remote Sensing of the European Seas. Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 3–22. ISBN 978-1-4020-6771-6. LCCN 2007942178. Retrieved August 28, 2009.
- ^ "NCMR - MAP". National Observatory of Athens. Archived from the original on August 28, 2009. Retrieved April 5, 2018.