
Back Llingües iroqueses AST ایروکوا دیللری AZB Іракезскія мовы Byelorussian Ирокезки езици Bulgarian Yezhoù irokwoyek Breton Llengües iroqueses Catalan Ирокез чĕлхисем CV Ieithoedd Irocwoiaidd Welsh Irokesische Sprachen German Irokeza lingvaro Esperanto
| Iroquoian | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Eastern North America |
| Ethnicity | Iroquoian peoples |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Iroquoian |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | iro |
| Glottolog | iroq1247 |
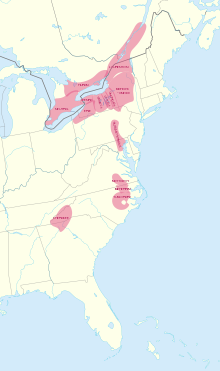
 Pre-European contact distribution of the Iroquoian languages. | |
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.[1]
As of 2020, almost all surviving Iroquoian languages are severely or critically endangered, with some languages having only a few elderly speakers remaining. The two languages with the most speakers, Mohawk (Kenien'kéha) in New York and Canada, and Cherokee in Oklahoma and North Carolina, are spoken by less than 10% of the populations of their nations.[2][3]
- ^ Mithun, Marianne. "Grammaticalization and Polysynthesis: Iroquoian" (PDF). Johannes-Gutenberg-Universität Mainz. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 14, 2020. Retrieved June 8, 2015.
- ^ "UNESCO Interactive Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger". unesco.org. Retrieved December 17, 2017.
- ^ "Iroquoian Languages". languagegeek.com. February 22, 2008. Archived from the original on February 23, 2012. Retrieved August 9, 2015.