
Back JWH-018 German JWH-018 Finnish JWH-018 French JWH-018 Croatian JWH-018 Italian JWH-018 Polish JWH-018 Russian JWH-018 Serbo-Croatian JWH-018 Serbian JWH-018 Swedish
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | |
| Drug class | Cannabinoid |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.163.574 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
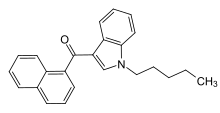
| Formula | C24H23NO |
| Molar mass | 341.454 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Solubility in water | hydrophobic, n/a mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
JWH-018 (1-pentyl-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole, NA-PIMO[3] or AM-678)[4] is an analgesic chemical from the naphthoylindole family that acts as a full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, with some selectivity for CB2. It produces effects in animals similar to those of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), a cannabinoid naturally present in cannabis, leading to its use in synthetic cannabis products that in some countries are sold legally as "incense blends".[5][6][7][8][9]
As a full agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, this chemical compound is classified as an analgesic medication.[10] The analgesic effects of cannabinoid ligands, mediated by CB1 receptors are well established in treatment of neuropathic pain, as well as cancer pain and arthritis.[10]
These compounds work by mimicking the body's naturally-produced endocannabinoid hormones such as 2-AG and anandamide (AEA), which are biologically active and can exacerbate or inhibit nerve signaling.[10] As the cause is poorly understood in chronic pain states, more research and development must be done before the therapeutic potential of this class of biologic compounds can be realized.[10]
- ^ "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (published 25 July 2023). 24 July 2023. Archived from the original on 27 August 2023. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- ^ "Substance Details JWH-018". Retrieved 22 January 2024.
- ^ Pulver B, Fischmann S, Gallegos A, Christie R (March 2023). "EMCDDA framework and practical guidance for naming synthetic cannabinoids". Drug Testing and Analysis. 15 (3): 255–276. doi:10.1002/dta.3403. PMID 36346325.
- ^ "Department of Justice :: Drug Enforcement Administration". 1 March 2011. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- ^ Zimmermann US, Winkelmann PR, Pilhatsch M, Nees JA, Spanagel R, Schulz K (2009). "Withdrawal Phenomena and Dependence Syndrome After the Consumption of "Spice Gold"". Dtsch Ärztebl Int. 106 (27): 464–467. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2009.0464. PMC 2719097. PMID 19652769.
- ^ Aung MM, Griffin G, Huffman JW, Wu M, Keel C, Yang B, et al. (2000). "Influence of the N-1 alkyl chain length of cannabimimetic indoles upon CB1 and CB2 receptor binding" (PDF). Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 60 (2): 133–140. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(99)00152-0. PMID 10940540. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2016.
- ^ US patent 6900236, Alexandros Makriyannis, Hongfeng Deng, "Cannabimimetic indole derivatives", issued 2005-05-31
- ^ US patent 7241799, Alexandros Makriyannis, Hongfeng Deng, "Cannabimimetic indole derivatives", issued 2007-07-10
- ^ Atwood BK, Huffman J, Straiker A, Mackie K (June 2010). "JWH018, a common constituent of 'Spice' herbal blends, is a potent and efficacious cannabinoid CB receptor agonist". British Journal of Pharmacology. 160 (3): 585–593. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00582.x. PMC 2931559. PMID 20100276.
- ^ a b c d Rani Sagar D, Burston JJ, Woodhams SG, Chapman V (December 2012). "Dynamic changes to the endocannabinoid system in models of chronic pain". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 367 (1607): 3300–11. doi:10.1098/rstb.2011.0390. PMC 3481532. PMID 23108548.