
Back مملكة كبادوكيا Arabic Regne de Capadòcia Catalan Reino de Capadocia Spanish پادشاهی کاپادوکیه Persian Ancien royaume de Cappadoce French Kerajaan Kapadokia ID Regno di Cappadocia Italian カッパドキア王国 Japanese Keyaniya Kapadokyayê Kurdish Kapadokya Krallığı Turkish
Kingdom of Cappadocia | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 331 BC–17 AD | |||||||||
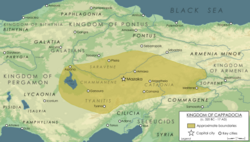 Kingdom of Cappadocia at its peak during the reign of Ariarathes V (163-130 BC) | |||||||||
| Status | Subject of the Kingdom of Pontus and Seleucid Empire Client kingdom of the Roman Republic and Roman Empire (95 BCE–17 AD) | ||||||||
| Capital | Mazaca (modern-day Kayseri, Turkey) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Greek (official) Old Persian (native and regional) Aramaic (initially used on coinage) | ||||||||
| Religion | Syncretic, incorporating Greek polytheism with Anatolian and Persian gods, as well as Zoroastrianism | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Basileus | |||||||||
• 331 – 322 BC (First Ariarathid king) | Ariarathes I | ||||||||
• 96 – c. 63 BC (First Ariobarzanid king) | Ariobarzanes | ||||||||
• 36 BC – 17 AD (last king) | Archelaus | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Founded by Ariarathes I | 331 BC | ||||||||
• Ariarathes IX deposed, Ariobarzanes I installed with military support from Sulla | 95 BC | ||||||||
• Ariarathes X deposed, Archelaus installed by Marc Antony | 36 BC | ||||||||
• Annexed by the Roman Empire under Emperor Tiberius. | 17 AD | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Cappadocia (Greek: Καππαδοκία) was a Hellenistic-era Iranian kingdom[1][2] centered in the historical region of Cappadocia in Asia Minor (present-day Turkey). It developed from the former Achaemenid satrapy of Cappadocia, and it was founded by its last satrap, Ariarathes (later Ariarathes I). Throughout its history, it was ruled by three families in succession; the House of Ariarathes (331–96 BC), the House of Ariobarzanes (96–36 BC), and lastly that of Archelaus (36 BC–17 AD). In 17 AD, following the death of Archelaus, during the reign of Roman emperor Tiberius (14–37 AD), the kingdom was incorporated as a Roman province.
- ^ Weiskopf 1990, pp. 780–786 "(...) Hellenistic-era Iranian kingdom (...) But all in all, Cappadocia remained an Iranian kingdom, one which developed from an Achaemenid satrapy."
- ^ McGing, Brian (1986). "Eupator in Asia before the first war with Rome". The Foreign Policy of Mithridates VI Eupator, King of Pontus. BRILL. p. 72. ISBN 978-9004075917.
As in Pontus the ruling family was of Iranian descent.