
Back Пергамскае царства Byelorussian Пергамско царство Bulgarian Regne de Pèrgam Catalan Βασίλειο της Περγάμου Greek Reino de Pérgamo Spanish Pergamon Estonian Regno di Pergamo Italian პერგამონის სამეფო Georgian Пергам патшалығы Kazakh 페르가몬 왕국 Korean
Kingdom of Pergamon | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| approx. 282 BC–129 BC | |||||||||||
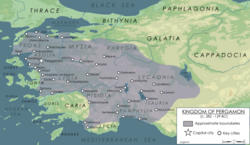 Pergamon in 188 BC | |||||||||||
| Capital | Pergamon (modern-day Bergama, İzmir, Turkey) | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Greek Lycian, Carian, Lydian | ||||||||||
| Religion | Greek Polytheism, Hellenistic Religion | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Basileus | |||||||||||
• 282–263 BC | Philetaerus | ||||||||||
• 263–241 BC | Eumenes I | ||||||||||
• 241–197 BC | Attalus I | ||||||||||
• 197–159 BC | Eumenes II | ||||||||||
• 160–138 BC | Attalus II | ||||||||||
• 138–133 BC | Attalus III | ||||||||||
• 133–129 BC | Eumenes III | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Hellenistic period | ||||||||||
• Philetaerus takes control of the city of Pergamon | approx. 282 BC | ||||||||||
• Attalus III bequeathed the kingdom to the Roman Republic | 133 BC | ||||||||||
• Incorporated into Roman province of Asia after the defeat of Eumenes III Aristonicus | 129 BC | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||

The Kingdom of Pergamon, Pergamene Kingdom, or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (/ˈætəlɪd/; Greek: Δυναστεία των Ατταλιδών, romanized: Dynasteía ton Attalidón).
The kingdom was a rump state that was created from the territory ruled by Lysimachus, a general of Alexander the Great. Philetaerus, one of Lysimachus' lieutenants, rebelled and took the city of Pergamon and its environs with him; Lysimachus died soon after in 281 BC. The new kingdom was initially in a vassal-like relationship of nominal fealty to the Seleucid Empire, but exercised considerable autonomy and soon became entirely independent. It was a monarchy ruled by Philetaerus's extended family and their descendants. It lasted around 150 years before being eventually absorbed by the Roman Republic during the period from 133–129 BC.