
Back Labradorsee Afrikaans بحر لبرادور Arabic Mar de Labrador AST Labrador dənizi Azerbaijani لابرادور دنیزی AZB Лабрадор диңгеҙе Bashkir Segara Labrador BAN Мора Лабрадор Byelorussian Лабрадорско море Bulgarian ল্যাব্রাডর সাগর Bengali/Bangla
| Labrador Sea | |
|---|---|
 Past sunset at Labrador Sea, off the coast of Paamiut, Greenland | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 61°N 56°W / 61°N 56°W |
| Type | Sea |
| Basin countries | Canada and Greenland |
| Max. length | c. 1,000 km (621 mi) |
| Max. width | c. 900 km (559 mi) |
| Surface area | 841,000 km2 (324,700 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 1,898 m (6,227 ft) |
| Max. depth | 4,316 m (14,160 ft) |
| References | [1][2] |
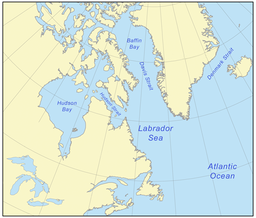
The Labrador Sea (French: mer du Labrador; Danish: Labradorhavet) is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, and northeast. It connects to the north with Baffin Bay through the Davis Strait.[3] It is a marginal sea of the Atlantic.[4][5]
The sea formed upon separation of the North American Plate and Greenland Plate that started about 60 million years ago and stopped about 40 million years ago. It contains one of the world's largest turbidity current channel systems, the Northwest Atlantic Mid-Ocean Channel (NAMOC), that runs for thousands of kilometers along the sea bottom toward the Atlantic Ocean.
The Labrador Sea is a major source of the North Atlantic Deep Water, a cold water mass that flows at great depth along the western edge of the North Atlantic.

- ^ "Labrador" (in Russian). Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
- ^ Wilson, R. C. L; London, Geological Society of (2001). "Non-volcanic rifting of continental margins: a comparison of evidence from land and sea". Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 187 (1): 77. Bibcode:2001GSLSP.187...77C. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.2001.187.01.05. ISBN 978-1-86239-091-1. S2CID 140632779.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica. "Labrador Sea". Retrieved 2008-02-03.
- ^ Calow, Peter (12 July 1999). Blackwell's concise encyclopedia of environmental management. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-632-04951-6. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- ^ Spall, Michael A. (2004). "Boundary Currents and Watermass Transformation in Marginal Seas". J. Phys. Oceanogr. 34 (5): 1197–1213. Bibcode:2004JPO....34.1197S. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(2004)034<1197:BCAWTI>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 128436726.
