
Back توزيع لابلاس Arabic Distribució de Laplace Catalan Laplace-Verteilung German Distribución de Laplace Spanish توزیع لاپلاس Persian Loi de Laplace (probabilités) French Distribuzione di Laplace Italian ラプラス分布 Japanese Laplaceverdeling Dutch Rozkład Laplace’a Polish
|
Probability density function 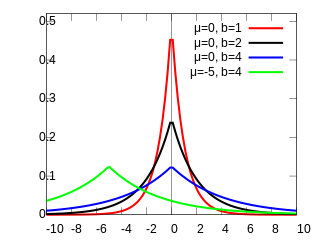 | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function  | |||
| Parameters |
location (real) scale (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Quantile | |||
| Mean | |||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
| MAD | |||
| Skewness | |||
| Excess kurtosis | |||
| Entropy | |||
| MGF | |||
| CF | |||
| Expected shortfall | [1] | ||
In probability theory and statistics, the Laplace distribution is a continuous probability distribution named after Pierre-Simon Laplace. It is also sometimes called the double exponential distribution, because it can be thought of as two exponential distributions (with an additional location parameter) spliced together along the abscissa, although the term is also sometimes used to refer to the Gumbel distribution. The difference between two independent identically distributed exponential random variables is governed by a Laplace distribution, as is a Brownian motion evaluated at an exponentially distributed random time[citation needed]. Increments of Laplace motion or a variance gamma process evaluated over the time scale also have a Laplace distribution.
- ^ a b Norton, Matthew; Khokhlov, Valentyn; Uryasev, Stan (2019). "Calculating CVaR and bPOE for common probability distributions with application to portfolio optimization and density estimation" (PDF). Annals of Operations Research. 299 (1–2). Springer: 1281–1315. doi:10.1007/s10479-019-03373-1. Retrieved 2023-02-27.




![{\displaystyle {\begin{cases}{\frac {1}{2}}\exp \left({\frac {x-\mu }{b}}\right)&{\text{if }}x\leq \mu \\[8pt]1-{\frac {1}{2}}\exp \left(-{\frac {x-\mu }{b}}\right)&{\text{if }}x\geq \mu \end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e7aca192c82e60e094aa5b7bee60f25de3dde43b)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{cases}\mu +b\ln \left(2F\right)&{\text{if }}F\leq {\frac {1}{2}}\\[8pt]\mu -b\ln \left(2-2F\right)&{\text{if }}F\geq {\frac {1}{2}}\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9c6ee6d1f9cb6b1b9f9070c4299a0e038d14d541)







