
Back Алаҭын бызшәа Abkhazian Latyn Afrikaans Lateinische Sprache ALS ሮማይስጥ Amharic Latín AN Læden ANG Latin ANN लैटिन भाषा ANP اللغة اللاتينية Arabic ܠܫܢܐ ܠܐܛܝܢܝܐ ARC
| Latin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | |
| Era | As a native language, from the 7th century BC to c. AD 700 |
Early form | |
| Latin alphabet (Latin script) | |
| Official status | |
| Regulated by | Pontifical Academy for Latin |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | la |
| ISO 639-2 | lat |
| ISO 639-3 | lat |
| Glottolog | impe1234lati1261 |
| Linguasphere | -ab, -ac 51-AAB-aa, -ab, -ac |
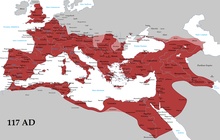 Greatest extent of the Roman Empire under Emperor Trajan (c. 117 AD) and the area governed by Latin speakers. Many languages other than Latin were spoken within the empire. | |
Latin (lingua Latina, pronounced [ˈlɪŋɡʷa ɫaˈtiːna], or Latinum [ɫaˈtiːnʊ̃]) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy.[1] Through the expansion of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire.
By the late Roman Republic, Old Latin had evolved into standardized Classical Latin. Vulgar Latin refers to the less prestigious colloquial registers, attested in inscriptions and some literary works such as those of the comic playwrights Plautus and Terence[2] and the author Petronius.
While often called a "dead language"[3], Latin did not undergo language death. By the 6th to 9th centuries, natural language change eventually resulted in Latin as a vernacular language evolving into distinct Romance languages in the large areas where it had come to be natively spoken. However, even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the early 19th century, by which time modern languages had supplanted it in common academic and political usage. Late Latin is the literary language from the 3rd century AD onward. No longer spoken as a native language, Medieval Latin was used across Western and Catholic Europe during the Middle Ages as a working and literary language from the 9th century to the Renaissance, which then developed a classicizing form, called Renaissance Latin. This was the basis for Neo-Latin which evolved during the early modern period. In these periods Latin was used productively and generally taught to be written and spoken, at least until the late seventeenth century, when spoken skills began to erode. It then became increasingly taught only to be read.
Latin grammar is highly fusional, with classes of inflections for case, number, person, gender, tense, mood, voice, and aspect. The Latin alphabet is directly derived from the Etruscan and Greek alphabets.
Latin remains the official language of the Holy See and the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church at the Vatican City. The church continues to adapt concepts from modern languages to Ecclesiastical Latin of the Latin language. Contemporary Latin is more often studied to be read rather than spoken or actively used.
Latin has greatly influenced the English language, along with a large number of others, and historically contributed many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin and Ancient Greek roots are heavily used in English vocabulary in theology, the sciences, medicine, and law.
- ^ Sandys, John Edwin (1910). A companion to Latin studies. University of Chicago Press. pp. 811–812.
- ^ Clark 1900, pp. 1–3
- ^ "Why is Latin a dead language? | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 5 August 2024.