
Back Lood(II)chloried Afrikaans كلوريد الرصاص الثنائي Arabic کولورید قورغوشون (II) AZB Chlorid olovnatý Czech Blei(II)-chlorid German Plumba (II) klorido Esperanto سرب(II) کلرید Persian Lyijykloridi Finnish Chlorure de plomb(II) French लेड(II) क्लोराइड Hindi

| |
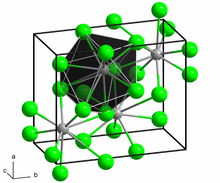 The crystal structure of PbCl2, in the unconventional crystallographic setting Pnam. This corresponds to the standard Pnma setting by switching the labels on the b and c axes.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Lead(II) chloride
Lead dichloride | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.950 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| PbCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 278.10 g/mol |
| Appearance | white odorless solid |
| Density | 5.85 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 501 °C (934 °F; 774 K) |
| Boiling point | 950 °C (1,740 °F; 1,220 K) |
| 0.99 g/100 mL (20 °C)[1] | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
1.7×10−5 (20 °C) |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in dilute HCl, ammonia; insoluble in alcohol Soluble in hot water as well as in presence of alkali hydroxide Soluble in concentrated HCl (>6M) |
| −73.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
2.199[2] |
| Structure[3] | |
| Orthorhombic, oP12 | |
| Pnma (No. 62) | |
a = 762.040 pm, b = 453.420 pm, c = 904.520 pm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
135.98 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-359.41 kJ/mol |
| Hazards[5] | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H332, H351, H360, H372, H410 | |
| P201, P261, P273, P304+P340, P308+P313, P312, P391 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LDLo (lowest published)
|
140 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral)[4] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lead(II) fluoride Lead(II) bromide Lead(II) iodide |
Other cations
|
Lead(IV) chloride Tin(II) chloride Germanium(II) chloride |
Related compounds
|
Thallium(I) chloride Bismuth chloride |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Lead(II) chloride (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite.
- ^ NIST-data review 1980 Archived 2014-02-11 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ Sass, Ronald L.; Brackett, E. B.; Brackett, T. E. (1963). "THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LEAD CHLORIDE". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 67 (12). American Chemical Society (ACS): 2863–2864. doi:10.1021/j100806a517. ISSN 0022-3654.
- ^ "Lead compounds (as Pb)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Classifications - CL Inventory". echa.europa.eu.
