
Back سرطان السحايا الرقيقة Arabic Meningeosis neoplastica German Méningite carcinomateuse French Meningoza Polish Канцероматоз мозговых оболочек Russian Ung thư màng não mềm Vietnamese
| Neoplastic meningitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Carcinomatous meningitis, leptomeningeal carcinoma, leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, leptomeningeal metastasis, meningeal carcinomatosis, meningeal metastasis, meningitis carcinomatosa, leptomeningeal disease (LMD), neoplastic meningitis |
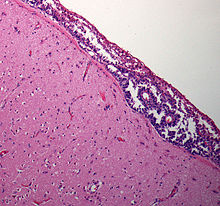 | |
| Meningeal carcinomatosis: tumor cell clusters in the subarachnoid space in a brain biopsy | |
| Specialty | Oncology, neurology |
Leptomeningeal cancer is a rare complication of cancer in which the disease spreads from the original tumor site to the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord.[1] This leads to an inflammatory response, hence the alternative names neoplastic meningitis (NM), malignant meningitis, or carcinomatous meningitis.[2][3] The term leptomeningeal (from the Greek lepto, meaning 'fine' or 'slight') describes the thin meninges, the arachnoid and the pia mater, between which the cerebrospinal fluid is located.[4] The disorder was originally reported by Eberth in 1870.[5] It is also known as leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, leptomeningeal disease (LMD), leptomeningeal metastasis, meningeal metastasis and meningeal carcinomatosis.
It occurs with cancers that are most likely to spread to the central nervous system.[6] The most common cancers to include the leptomeninges are breast cancer, lung cancer, and melanomas because they can metastasize to the subarachnoid space[7] in the brain which offers a hospitable environment for the growth of metastatic tumor cells.[7][8] Individuals whose cancer has spread to an area of the brain known as the posterior fossa have a greater risk of developing a leptomeningeal cancer.[9] The condition can also arise from primary brain tumor like medulloblastoma.
Leptomeningeal disease is becoming more evident because cancer patients are living longer and many chemotherapies cannot reach sufficient concentrations in the spinal fluid to kill the tumor cells.[7]
- ^ "Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Practice Essentials, Background, Pathophysiology". 6 December 2017.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Neoplastic meningitis". NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. National Cancer Institute. Retrieved 31 July 2018.
- ^ "Leptomeningeal Tumor". Florida Hospital. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
- ^ Lukas, Rimas V.; Buerki, Robin; Mrugala, Maciej M. (16 August 2016). "Management of Leptomeningeal Disease From Solid Tumors". Oncology Vol 30 No 8. 30.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Serious Cancer Complication". www.princetonbrainandspine.com. Retrieved 2018-04-20.
- ^ staff, MD Anderson. "New hope for leptomeningeal disease care". www.mdanderson.org. Retrieved 2018-04-20.
- ^ a b c "Carcinomatous Meningitis: It Does Not Have to Be a Death Sentence | Cancer Network". Oncology. ONCOLOGY Vol 16 No 2. 16 (2). February 2002. Retrieved 2018-04-20.
- ^ Grossman, S. A.; Krabak, M. J. (April 1999). "Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 25 (2): 103–119. doi:10.1053/ctrv.1999.0119. ISSN 0305-7372. PMID 10395835.
- ^ "Causes of Leptomeningeal Tumor". Florida Hospital. Retrieved 2018-04-20.