
Back Luxemburgs Afrikaans Luxemburgische Sprache ALS ሉክሰምበርግኛ Amharic Idioma luxemburgués AN लक्ज़मबर्गी भाषा ANP اللغة اللوكسمبورغية Arabic اللوكسمبورغيه ARZ Idioma luxemburgués AST Lüksemburq dili Azerbaijani Luxnbuagisch BAR
| Luxembourgish | |
|---|---|
| Lëtzebuergesch | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈlətsəbuəjəʃ] |
| Native to | Luxembourg; Saarland and north-west Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany; Arelerland and Saint-Vith district, Belgium; Moselle department, France |
| Region | Western Europe |
| Ethnicity | Luxembourgers |
Native speakers | 300,000 (2024)[1] |
Early forms | Proto-Indo-European
|
| Official status | |
Official language in | Luxembourg |
Recognised minority language in | Belgium (recognised by the French Community of Belgium) |
| Regulated by | Council for the Luxembourgish Language |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | lb |
| ISO 639-2 | ltz |
| ISO 639-3 | ltz |
| Glottolog | luxe1243 |
| Linguasphere | 52-ACB-db |
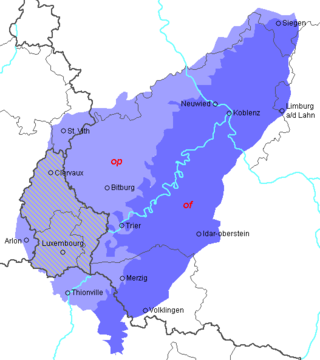 The area where Luxembourgish (pale indigo) and other dialects of Moselle Franconian (medium indigo) are spoken. The internal isogloss for words meaning "on, at", i.e. op and of, is also shown (Standard German: auf). | |
Luxembourgish (/ˈlʌksəmbɜːrɡɪʃ/ LUK-səm-bur-ghish; also Luxemburgish,[2] Luxembourgian,[3] Letzebu(e)rgesch;[4] endonym: Lëtzebuergesch [ˈlətsəbuəjəʃ] ) is a West Germanic language that is spoken mainly in Luxembourg. About 300,000 people speak Luxembourgish worldwide.[5]
The language is standardized and officially the national language of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. As such, Luxembourgish is different from the German language also used in the Grand Duchy. The German language exists in a national standard variety of Luxembourg, which is slightly different from the standard varieties in Germany, Austria or Switzerland. Another important language of Luxembourg is French, which had a certain influence on both the national language Luxembourgish and the Luxembourg national variety of German. Luxembourgish, German and French are the three official languages (Amtssprachen) of Luxembourg.
As a standard form of the Moselle Franconian language, Luxembourgish has similarities with other High German dialects and the wider group of West Germanic languages. The status of Luxembourgish as the national language of Luxembourg and the existence there of a regulatory body[6] have removed Luxembourgish, at least in part, from the domain of Standard German, its traditional Dachsprache. It is also related to the Transylvanian Saxon dialect spoken by the Transylvanian Saxons in Transylvania, contemporary central Romania.
- ^ Luxembourgish at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ "Luxemburgish – definition of Luxemburgish in English from the Oxford dictionary". Archived from the original on 7 July 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^
- Kas Deprez (1997). Michael G. Clyne (ed.). "Diets, Nederlands, Nederduits, Hollands, Vlaams, Belgisch-Nederlands". Undoing and Redoing Corpus Planning. Walter de Gruyter: 249. ISBN 9783110155099.
- Bengt Skoog (1983). Immigrants and Cultural Development in European Towns. Council for Cultural Co-operation. p. 51. ISBN 9789287102393.
- National Geographic Society (2005). Our Country's Regions: Outline maps. Macmillan/McGraw-Hill. p. 59. ISBN 9780021496259.
- ^ "Letzeburgesch – definition of Lëtzeburgesch in English from the Oxford dictionary". Archived from the original on 15 September 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ "Le nombre de locuteurs du luxembourgeois revu à la hausse" (PDF). Retrieved 8 November 2012.
- ^ "Law establishing the Conseil Permanent de la Langue Luxembourgeoise (CPLL)" (PDF).